Antibacterial Composites Based on Alginate/Egg White and ZnO Nanoparticles with the Addition of Essential Oils
- PMID: 40558758
- PMCID: PMC12191582
- DOI: 10.3390/gels11060459
Antibacterial Composites Based on Alginate/Egg White and ZnO Nanoparticles with the Addition of Essential Oils
Abstract
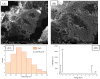
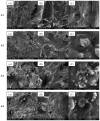
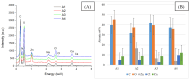
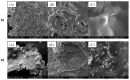
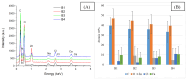
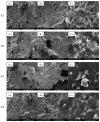
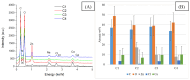
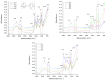
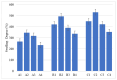
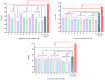
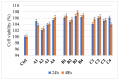
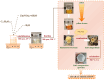
A series of hydrogels containing sodium alginate at different concentrations (2%, 3%, and 4%) and egg white were prepared through ionic cross-linking with calcium chloride (CaCl2) to obtain composite dressing materials. ZnO nanoparticles coated with eucalyptus or lavender essential oil were introduced into the hydrogel matrix to enhance antibacterial properties. The resulting hydrogels were freeze-dried to enhance mechanical properties, increase the porosity of the dressing, and facilitate further evaluations. A variety of analytical methods, including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) were employed to characterize the composites. The developed composites exhibited high porosity and a swelling degree exceeding 200% after 3 days. Additionally, water absorption capacity increased with higher alginate concentrations in the samples. Furthermore, they demonstrated significant antibiofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, and Escherichia coli, with the samples containing 4% alginate showing the best results.
Keywords: alginate composite; antibacterial materials; egg white; wound dressing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dressings and topical agents for the management of open wounds after surgical treatment for sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013439. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013439.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593897 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an Alginate Gel Composite with Antibacterial Properties Capable of Binding Calcium-Based Residual Stone Fragments in Endoscopic Stone Surgery.J Endourol. 2025 Jun;39(6):585-593. doi: 10.1089/end.2024.0765. Epub 2025 Apr 8. J Endourol. 2025. PMID: 40197160
-
Hydrogel dressings for venous leg ulcers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 5;8(8):CD010738. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010738.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35930364 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel dressings for donor sites of split-thickness skin grafts.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 16;8(8):CD013570. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013570.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37584338 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the molar mass of chitosan and film casting solvents on the properties of chitosan films loaded with Mentha spicata essential oil for potential application as wound dressing.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2024 Dec;35(18):2807-2828. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2024.2390752. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2024. PMID: 39167543
References
-
- Bueno J., Demirci F., Baser K.H.C. The Microbiology of Skin, Soft Tissue, Bone and Joint Infections. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2017. Antimicrobial Strategies in Novel Drug Delivery Systems; pp. 271–286. - DOI
-
- Kaushik M., Niranjan R., Thangam R., Madhan B., Pandiyarasan V., Ramachandran C., Oh D.-H., Venkatasubbu G.D. Investigations on the antimicrobial activity and wound healing potential of ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019;479:1169–1177. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.189. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

