MedSAM/MedSAM2 Feature Fusion: Enhancing nnUNet for 2D TOF-MRA Brain Vessel Segmentation
- PMID: 40558801
- PMCID: PMC12194608
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging11060202
MedSAM/MedSAM2 Feature Fusion: Enhancing nnUNet for 2D TOF-MRA Brain Vessel Segmentation
Abstract
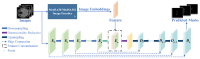
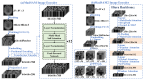
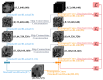
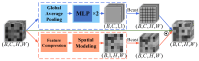
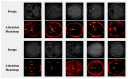
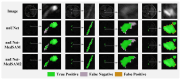
Accurate segmentation of brain vessels is critical for diagnosing cerebral stroke, yet existing AI-based methods struggle with challenges such as small vessel segmentation and class imbalance. To address this, our study proposes a novel 2D segmentation method based on the nnUNet framework, enhanced with MedSAM/MedSAM2 features, for arterial vessel segmentation in time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA) brain slices. The approach first constructs a baseline segmentation network using nnUNet, then incorporates MedSAM/MedSAM2's feature extraction module to enhance feature representation. Additionally, focal loss is introduced to address class imbalance. Experimental results on the CAS2023 dataset demonstrate that the MedSAM2-enhanced model achieves a 0.72% relative improvement in Dice coefficient and reduces HD95 (mm) and ASD (mm) from 48.20 mm to 46.30 mm and from 5.33 mm to 4.97 mm, respectively, compared to the baseline nnUNet, showing significant enhancements in boundary localization and segmentation accuracy. This approach addresses the critical challenge of small vessel segmentation in TOF-MRA, with the potential to improve cerebrovascular disease diagnosis in clinical practice.
Keywords: MedSAM; MedSAM2; TOF-MRA; brain vessel segmentation; nnUNet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Automated segmentation of thoracic aortic lumen and vessel wall on three-dimensional bright- and black-blood magnetic resonance imaging using nnU-Net.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2025 Jun 11;27(2):101923. doi: 10.1016/j.jocmr.2025.101923. Online ahead of print. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2025. PMID: 40513884
-
Accuracy of an nnUNet Neural Network for the Automatic Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysms, Their Parent Vessels, and Major Cerebral Arteries from MRI-TOF.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2025 May 2;46(5):956-963. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8607. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2025. PMID: 39578106
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.Health Technol Assess. 2007 May;11(20):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-184. doi: 10.3310/hta11200. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17462170
-
COSTA: A Multi-Center TOF-MRA Dataset and a Style Self-Consistency Network for Cerebrovascular Segmentation.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2024 Dec;43(12):4442-4456. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3424976. Epub 2024 Dec 2. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39012728
-
Duplex ultrasound for diagnosing symptomatic carotid stenosis in the extracranial segments.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 11;7(7):CD013172. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013172.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35815652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feigin V.L., Abate M.D., Abate Y.H., ElHafeez S.A., Abd-Allah F., Abdelalim A., Abdelkader A., Abdelmasseh M., Abd-Elsalam S., Abdi P., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024;23:973–1003. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00369-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coppenrath E.M., Lummel N., Linn J., Lenz O., Habs M., Nikolaou K., Reiser M.F., Dichgans M., Pfefferkorn T., Saam T. Time-of-flight angiography: A viable alternative to contrast-enhanced MR angiography and fat-suppressed T1w images for the diagnosis of cervical artery dissection? Eur. Radiol. 2013;23:2784–2792. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2891-1. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

