The Dynamic Interactions of m6A Modification and R-Loops: Implications for Genome Stability
- PMID: 40558832
- PMCID: PMC12192009
- DOI: 10.3390/epigenomes9020021
The Dynamic Interactions of m6A Modification and R-Loops: Implications for Genome Stability
Abstract
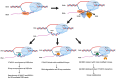
R-loops, three-stranded RNA-DNA hybrid nucleic acid structures, are recognized for their roles in both physiological and pathological processes. Regulation of R-loops is critical for genome stability as disruption of R-loop homeostasis can lead to aberrant gene expression, replication stress, and DNA damage. Recent studies suggest that the RNA modification, N6-methyladenosine (m6A), can modify R-loops and the writers, erasers, and readers of m6A are involved in the dynamic regulation of R-loops. Here, we discuss the reported functions of various m6A regulatory proteins in relation to R-loops, highlighting their distinct roles in recognizing and modulating the formation, stability, and resolution of these structures. We further examine the functional implications of m6A and R-loop interaction in human diseases, with a particular emphasis on their roles in cancer.
Keywords: DNA damage; R-loops; genome stability; m6A RNA modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

