The Insecticide Imidacloprid Promotes Algal Growth in Absence of Zooplankton
- PMID: 40558873
- PMCID: PMC12194706
- DOI: 10.3390/jox15030090
The Insecticide Imidacloprid Promotes Algal Growth in Absence of Zooplankton
Abstract
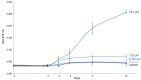
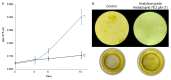
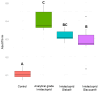
Imidacloprid, a systemic neonicotinoid insecticide, exerts its neurotoxic effects by binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system. In this study, we examined the effects of commercial imidacloprid formulations on the growth of Chlorella vulgaris and other algal species, comparing these responses with those induced by plant hormones. Our results demonstrate that formulated imidacloprid stimulates C. vulgaris growth at concentrations as low as 7.82 μM, with a more pronounced effect than certain phytohormones. We observed similar growth-enhancing effects in other algal species exposed to imidacloprid. Notably, pure imidacloprid induced equivalent growth responses in C. vulgaris, confirming that the observed stimulation results from the active ingredient itself rather than formulation adjuvants. Given its insecticidal mode of action, potential worst-case aquatic contamination scenarios with imidacloprid may lead to significant increases in algal biomass through both direct (growth stimulation) and indirect (reduction of zooplankton grazing pressure) mechanisms.
Keywords: algae; growth promotion; hormones; imidacloprid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exercise interventions on health-related quality of life for people with cancer during active treatment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;2012(8):CD008465. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008465.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22895974 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Interventions for recruiting smokers into cessation programmes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD009187. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009187.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235672 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Indoor residual spraying for preventing malaria in communities using insecticide-treated nets.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD012688. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012688.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35038163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sheets L.P. Hayes’ Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 2010. Imidacloprid: A neonicotinoid insecticide; pp. 2055–2064.
-
- Senn R., Hofer D., Thieme T., Zang L. Method for Improving Plant Growth. No. 6,753,296. U.S. Patent. 2004 June 22;
-
- Gonias E.D., Oosterhuis D.M., Bibi A.C. How the insecticide Trimax TM improves the growth and yield of cotton; Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conference; San Antonio, TX, USA. 3–6 January 2006.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

