Virulence Characterization of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China in 2020 Using Wheat Yr Single-Gene Lines
- PMID: 40558959
- PMCID: PMC12194282
- DOI: 10.3390/jof11060447
Virulence Characterization of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China in 2020 Using Wheat Yr Single-Gene Lines
Abstract
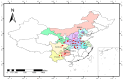
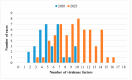
Wheat stripe (yellow) rust, caused by the fungus Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst), is one of the most threatening wheat diseases worldwide. Monitoring the virulence of Pst population is essential for managing wheat stripe rust. In this study, 18 wheat Yr single-gene lines were used to identify the virulence patterns of 67 isolates collected from 13 provinces in China in 2020, from which 33 Pst races were identified. The frequency of virulence to different Yr genes varied from 1.49% to 97.01%, with 4.48% to Yr1, 26.87% to Yr6, 11.94% to Yr7, 95.52% to Yr8, 19.40% to Yr9, 11.94% to Yr17, 2.99% to Yr24, 35.82% to Yr27, 38.81% to Yr43, 97.01% to Yr44, 8.96% to YrSP, 1.49% to Yr85, 95.52% to YrExp2, and 7.46% to Yr76. None of the isolates were virulent to Yr5, Yr10, Yr15, and Yr32. Among the 33 races, PstCN-062 (with virulence to Yr8, Yr44, and YrExp2) and PstCN-001 (with virulence to Yr8, Yr43, Yr44, and YrExp2) were the prevalent races, with frequencies of 28.36% and 11.94%, respectively. These results provide valuable information for breeding resistant wheat cultivars for controlling stripe rust.
Keywords: Triticum aestivum; pathogen; race identification; resistance genes; stripe rust; virulence diversity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wellings C.R. Global status of stripe rust: A review of historical and current threats. Euphytica. 2011;179:129–141. doi: 10.1007/s10681-011-0360-y. - DOI
-
- Kang Z.S., Wang X.J., Zhao J., Tang C.L., Huang L.L. Advances in research of pathogenicity and virulence variation of the wheat stripe rust fungus Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015;48:3439–3453.
-
- Awais M., Ma J., Chen W., Zhang B., Turakulov K.S., Li L., Egamberdieva D., Karimjonovich M.S., Kang Z., Zhao J. Molecular genotyping revealed the gene flow of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici clonal lineage from Uzbekistan of Central Asia to Xinjiang of China. Phytopathol. Res. 2025;7:2. doi: 10.1186/s42483-024-00290-5. - DOI
-
- Huang L., Chen X., Dong Y., Huang W., Ma H., Zhang H., Xu Y., Wang J. Dynamic Analysis of Regional Wheat Stripe Rust Environmental Suitability in China. Remote Sens. 2023;15:2021. doi: 10.3390/rs15082021. - DOI
-
- Zhao J., Kang Z. Fighting wheat rusts in China: A look back and into the future. Phytopathol. Res. 2023;5:6. doi: 10.1186/s42483-023-00159-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

