Managing African Armyworm Outbreaks in Sub-Saharan Africa: Current Strategies and Future Directions
- PMID: 40559075
- PMCID: PMC12193339
- DOI: 10.3390/insects16060645
Managing African Armyworm Outbreaks in Sub-Saharan Africa: Current Strategies and Future Directions
Abstract
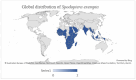
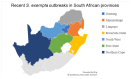
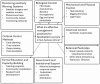
The African armyworm Spodoptera exempta (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) is a significant pest that affects cereal crops and pasture grasses in sub-Saharan Africa. This migratory pest causes extensive defoliation, which can result in significant yield losses, particularly in maize. This review focuses on the recent outbreaks of the African armyworm and identifies key factors contributing to its success across sub-Saharan Africa. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective and sustainable pest management strategies. This review emphasizes the importance of innovative technologies and data-driven approaches in managing pest outbreaks and underscores the need to implement technology-enabled integrated pest management (IPM) strategies to control the African armyworm effectively.
Keywords: innovative tools; integrated pest management; migratory pest; pest control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rose J.W., Dewhurst C.F., Page W.W. The African Armyworm Handbook: The Status, Biology, Ecology, Epidemiology and Management of Spodoptera exempta (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) 2nd ed. Natural Resources Institute, University of Greenwich; London, UK: 2000.
-
- Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International (CABI) Spodoptera exempta (Black armyworm). CABI Compendium, 29809 Datasheet, 6 April 2020. [(accessed on 29 April 2025)]. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.1079/cabicompendium.29809. - DOI
-
- Fox K.J. Migrant Lepidoptera in New Zealand 1972–1973. N. Z. Entomol. 1973;5:268–271. doi: 10.1080/00779962.1973.9723017. - DOI
-
- Baker G.L. An outbreak of Spodoptera exempta (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the highlands of Papua New Guinea. PNG Agric. J. 1978;29:11–25.
-
- Haggis M.J. Distribution, Frequency of Attack and Seasonal Incidence of the African Armyworm Spodoptera exempta (Walk.) (Lep.: Noctuidae), with Particular Reference to Africa and Southwestern Arabia. Tropical Development and Research Institute; London, UK: 1984.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

