PRP Therapy for Stress Urinary Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse: A New Frontier in Personalized Treatment?
- PMID: 40559077
- PMCID: PMC12194431
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm15060214
PRP Therapy for Stress Urinary Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse: A New Frontier in Personalized Treatment?
Abstract
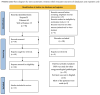
Background: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and stress incontinence (SUI) are very common medical conditions, affecting women's quality of life worldwide. Current surgical and conservative therapies often yield variable outcomes and carry risks of complications or recurrence. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has emerged as a promising regenerative approach in various medical disciplines. Its application in urogynecology remains relatively new and emerging. The objective of this study was to review and consolidate existing evidence regarding the application of PRP injections for treating POP and/or SUI. Methods: This scoping review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR). The search strategy included MEDLINE (PubMed), Web of Science, and Scopus databases, covering articles published up to February 2025, with no restrictions on publication date. Results: We included in our review a total of 13 manuscripts and 320 patients at the end of the screening process. A total of ten SUI studies, comprising 273 patients, and three POP studies, involving 47 patients, satisfied all the review criteria. Both clinical entities reported high subjective improvement following PRP treatment. Moreover, PRP appeared to have no significant adverse effects. Conclusions: Our scoping review suggests that PRP may have potential benefits in the treatment of POP and SUI. Nevertheless, the current evidence on its application in this area remains limited. Therefore, well-designed, large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with extended follow-up periods are urgently needed, in the era of personalized medicine.
Keywords: PRP injections; platelet-rich plasma; prolapse; stress urinary incontinence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Haylen B.T., Maher C.F., Barber M.D., Camargo S., Dandolu V., Digesu A., Goldman H.B., Huser M., Milani A.L., Moran P.A., et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) Joint Report on the Terminology for Female Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP) Int. Urogynecol. J. 2016;27:165–194. doi: 10.1007/s00192-015-2932-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials