Evaluation of Perioperative Risk Factors for Infection by Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Patients Undergoing Liver Transplantation
- PMID: 40559103
- PMCID: PMC12194424
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm15060240
Evaluation of Perioperative Risk Factors for Infection by Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Patients Undergoing Liver Transplantation
Abstract
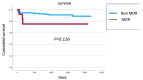
Background: Liver transplantation (LT) is a critical intervention for patients with end-stage liver disease. Infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB) significantly worsen post-transplant outcomes. The main objective of this study was to analyze perioperative risk factors associated with MDRB infections within six months following LT. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 133 medical records of patients who underwent liver transplantation between October 2018 and May 2022. Data collected included the presence of MDRB colonization and infection, as well as various perioperative variables. These were analyzed to identify potential risk factors for MDRB infection and colonization. Results: Univariate analysis identified several perioperative variables associated with MDRB infection within six months after LT. Multivariate logistic regression revealed that pre-transplant MDRB colonization (OR 5.72, 95% CI 1.7-18.7, p = 0.005) and the requirement for dialysis during postoperative ICU stay (OR 6.42, 95% CI 1.7-23.4, p = 0.009) were independent risk factors for developing MDRB infections. MDRB infection occurred in 9.4% of patients and was not significantly associated with increased mortality (p = 0.126). Conclusions: These findings contribute to a better understanding of the epidemiology and pathophysiology of MDRB infections in the postoperative period of liver transplantation. This knowledge is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies that may improve outcomes in this patient population.
Keywords: bacterial infection; liver transplantation; multidrug-resistant; perioperative risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Huang Y.S., Lai L.C., Chen Y.A., Lin K.Y., Chou Y.H., Chen H.C., Wang S.-S., Wang J.-T., Chang S.-C. Colonization with multidrug-resistant organisms among healthy adults in the community setting: Prevalence, risk factors, and composition of gut microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2020;11:1402. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources