Impacts of Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Soil-Plant System and Their Potential Agricultural Applications
- PMID: 40559314
- PMCID: PMC12195988
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15120950
Impacts of Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Soil-Plant System and Their Potential Agricultural Applications
Abstract
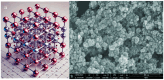
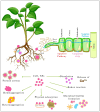
Cerium dioxide nanoparticles (CeO2-NPs) are increasingly used in various industrial applications, leading to their inevitable release into the environment including the soil ecosystem. In soil, CeO2-NPs are taken up by plants, translocated, and accumulated in plant tissues. Within plant tissues, CeO2-NPs have been shown to interfere with critical metabolic pathways, which may affect plant health and productivity. Moreover, their presence in soil can influence soil physico-chemical and biological properties, including microbial communities within the rhizosphere, where they can alter microbial physiology, diversity, and enzymatic activities. These interactions raise concerns about the potential disruption of plant-microbe symbiosis essential for plant nutrition and soil health. Despite these challenges, CeO2-NPs hold potential as tools for enhancing crop productivity and resilience to stress, such as drought or heavy metal contamination. However, understanding the balance between their beneficial and harmful effects is crucial for their safe application in agriculture. To date, the overall impact of CeO2-NPs on soil -plant system and the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Therefore, this review analyses the recent research findings to provide a comprehensive understanding of the fate of CeO2-NPs in soil-plant systems and the implications for soil health, plant growth, and agricultural productivity. As the current research is limited by inconsistent findings, often due to variations in experimental conditions, it is essential to study CeO2-NPs under more ecologically relevant settings. This review further emphasizes the need for future research to assess the long-term environmental impacts of CeO2-NPs in soil-plant systems and to develop guidelines for their responsible use in sustainable agriculture.
Keywords: agricultural applications; cerium dioxide nanoparticles; crop production; plant growth; soil ecosystem; transformations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Collin B., Auffan M., Johnson A.C., Kaur I., Keller A.A., Lazareva A., Lead J.R., Ma X., Merrifield R.C., Svendsen C., et al. Environmental release, fate and ecotoxicological effects of manufactured ceria nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2014;1:533–548. doi: 10.1039/C4EN00149D. - DOI
-
- Khan Y., Sadia H., Ali Shah S.Z., Khan M.N., Shah A.A., Ullah N., Ullah M.F., Bibi H., Bafakeeh O.T., Khedher N.B., et al. Classification, Synthetic, and Characterization Approaches to Nanoparticles, and Their Applications in Various Fields of Nanotechnology: A Review. Catalysts. 2022;12:1386. doi: 10.3390/catal12111386. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials