Treatment-Associated Neuroplastic Changes in People with Stroke-Associated Ataxia-An fMRI Study
- PMID: 40559323
- PMCID: PMC12196493
- DOI: 10.3390/neurolint17060084
Treatment-Associated Neuroplastic Changes in People with Stroke-Associated Ataxia-An fMRI Study
Abstract
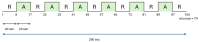
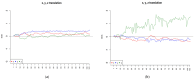
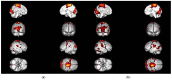
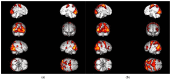
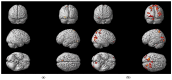
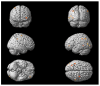
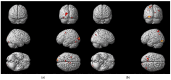
Background/Objectives: In consideration of the significance of the pursuit of training-induced neuroplastic changes in the stroke population, who are reliant on neurorehabilitation treatment for the restoration of neuronal function, the objectives of this trial were to investigate fMRI paradigms for acute stroke patients with ataxic symptoms, to follow up on changes in motor function and balance due to recovery and rehabilitation, and to investigate the different effects of two treatment methods on neuronal plasticity. Methods: Therefore, fMRI-paradigms foot tapping and the motor imagery (MI) of a balancing task (tandem walking) were employed. Results: The paradigms investigated were suitable for ataxic stroke patients to monitor changes in neuroplasticity while revealing increased activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) and the cerebellum over 3 months of treatment. Furthermore, analysis of the more complex balance task revealed augmented activation of association areas due to training. Coordination exercises, constituting a specific treatment of ataxic symptoms, indicate more consolidated brain activations, corresponding to a faster motor learning process. Activation within Brodmann Area 7 has been prominent among all paradigms, indicating a special importance of this region for coordinative functions. Conclusions: Further studies are needed to confirm our results in larger patient groups. Clinical Trial Registration: German Clinical Trials Registry (drks.de). Identifier: DRKS00020825. Registered 16.07.2020.
Keywords: acute stroke; ataxia; balance; coordination exercises; fMRI; foot tapping; motor imagery; neurorehabilitation; plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD000213. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000213. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 07;(4):CD000213. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000213.pub2. PMID: 12917889 Updated.
-
Interventions for motor rehabilitation in people with transtibial amputation due to peripheral arterial disease or diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 5;6(6):CD013711. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013711.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37276273 Free PMC article.
-
Neuraminidase inhibitors for preventing and treating influenza in healthy adults and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD008965. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008965.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 10;(4):CD008965. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008965.pub4. PMID: 22258996 Updated.
-
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving activities of daily living, and physical and cognitive functioning, in people after stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 21;3(3):CD009645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009645.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 11;11:CD009645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009645.pub4. PMID: 26996760 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The effect of time spent in rehabilitation on activity limitation and impairment after stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 25;10(10):CD012612. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012612.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34695300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feigin V.L., Forouzanfar M.H., Krishnamurthi R., Mensah G.A., Connor M., Bennett D.A., Moran A.E., Sacco R.L., Anderson L., Truelsen T., et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990-2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2014;383:245–254. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61953-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belas Dos Santos M., Barros de Oliveira C., Dos Santos A., Garabello Pires C., Dylewski V., Arida R.M. A Comparative Study of Conventional Physiotherapy versus Robot-Assisted Gait Training Associated to Physiotherapy in Individuals with Ataxia after Stroke. Behav. Neurol. 2018;2018:2892065. doi: 10.1155/2018/2892065. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

