Application of Craniosacral Therapy Versus Blood Levels of Corticoliberin and Oxytocin in Male Firefighters Exposed to Occupational Stress-A Randomised Control Trial
- PMID: 40559398
- PMCID: PMC12195089
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo15060374
Application of Craniosacral Therapy Versus Blood Levels of Corticoliberin and Oxytocin in Male Firefighters Exposed to Occupational Stress-A Randomised Control Trial
Abstract
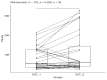
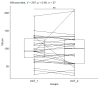
Background: Firefighters' work exposes them to high levels of stress. Oxytocin (OXT) and corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) are hormones released in response to stress. Prolonged exposure to stress can have negative effects, such as increased blood pressure and glucose levels, and a weakened immune system. Methods: This study involved 57 fire department cadets, randomly divided into craniosacral therapy (CS) and contralateral therapy (CO) groups. This study aimed to check whether 5-week craniosacral therapy affects CRH and OXT levels, determined from blood. Results: For the CS group, CRH_1 and CRH_2 showed slight increases in median values, 1.73 vs. 2.16, and OXT_1 and OXT_2 showed significant increases in median values, 54.71 vs. 57.77. Spearman's correlation coefficient for CRH_1 vs. OXT_1 was r = 0.26, p = 0.124; similarly, for CRH_2 vs. OXT_2 was r = -0.02, p = 0.920; for CRH_ 1 vs. CRH_2 was r = 0.25, p = 0.173; and for OXT_1 vs. OXT_2 was r = 0.77, p < 0.00001. The values of the point statistics for CRH were similar in CO_1 and CS_1. After the end of therapy, in the CS_2 group, the values of the point statistics were greater than those for the CO_2 group. The median values for oxytocin in the CO_1 group were greater than those in the CS_1 group. After the end of therapy, in the CO_2 group, the values of the scoring statistics were smaller than those for the CS_2 group. The effect of the intervention in the CS group and the CO group showed a significance of p = 0.0003 and p = 0.023. Conclusions: After the end of therapy, a significant increase in OXT levels was observed, as well as a slight increase in CRH levels.
Keywords: alternative medicine; corticotrophin-releasing hormone; craniosacral therapy; firefighters; oxytocin; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

