SARS-CoV-2 in Asthmatic Children: Same Consequences in Different Endotypes?
- PMID: 40559430
- PMCID: PMC12194914
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo15060406
SARS-CoV-2 in Asthmatic Children: Same Consequences in Different Endotypes?
Abstract
During the early stages of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic, concerns arose regarding the susceptibility of asthmatic children, one of the most common chronic conditions in childhood and a major cause of hospitalization in pediatric settings. Unexpectedly, evidences showed milder clinical courses and fewer asthma exacerbations in these patients, even if cases of critical and fatal infection, often related to specific clinical features of the patient, are not negligible. In this regard, obesity is considered not only an important comorbidity in patients with difficult-to-treat asthma but also a risk factor for more severe forms of COVID-19. These observations are of even greater concern in the context of an increase in childhood obesity that began even before the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and has continued also as a consequence of it. Given asthma's heterogeneity, especially in children, an endotype-based approach is crucial. This is possible through a detailed analysis of the complex metabolic pathways that correlate asthma, COVID-19 infection and obesity thanks to new high-through-put technologies, especially metabolomics, which with minimally invasive sampling, including on exhaled breath condensate (EBC), can provide precise and unbiased evidence in support of existing endotypes, making it possible to identify not only the most vulnerable individuals and thus risk stratification through specific biomarkers, but also new molecular and therapeutic targets. This review explores asthma endotypes by highlighting their shared immunometabolic pathways with COVID-19. Findings suggest that metabolomics could enable more accurate risk stratification and guide personalized interventions during viral pandemics, especially in the presence of relevant comorbidities such as obesity.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; asthma endotypes; metabolomics; obesity; pediatric asthma; precision medicine; risk stratification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
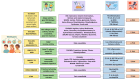
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Non-pharmacological measures implemented in the setting of long-term care facilities to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections and their consequences: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 15;9(9):CD015085. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015085.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34523727 Free PMC article.
-
Shared decision-making for people with asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 3;10(10):CD012330. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012330.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28972652 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve inhaler technique for people with asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 13;3(3):CD012286. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012286.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28288272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson D.J., Busse W.W., Bacharier L.B., Kattan M., O’Connor G.T., Wood R.A., Visness C.M., Durham S.R., Larson D., Esnault S., et al. Association of respiratory allergy, asthma, and expression of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020;146:203–206.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holley A.B. Medscape: Does Asthma Lead to Worse COVID-19 Outcomes? Updated 2020. [(accessed on 4 July 2021)]. Available online: https://www.medscape.com.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

