Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) as Prognostic Markers of COVID-19 Disease Irrespective of Immunosuppression Status: A Case-Control Retrospective Single-Center Study
- PMID: 40559558
- PMCID: PMC12196196
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens14060550
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) as Prognostic Markers of COVID-19 Disease Irrespective of Immunosuppression Status: A Case-Control Retrospective Single-Center Study
Abstract
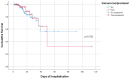
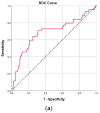
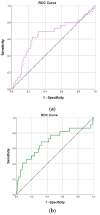
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) have been studied as predictors for severe COVID-19 outcomes. The aim of the present study is to identify prognostic cut-off values of NLR and PLR for intubation and death in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, with or without immunosuppression. From June 2021 to December 2022, we retrospectively analyzed 393 consecutively admitted COVID-19 patients, who were divided in two cohorts according to immunosuppression status (hematological malignancy and/or autoimmune condition vs. non-immunocompromised), using a propensity score-matching in 1:2 ratio. Higher NLR and PLR values were observed on days 1 and 4 for severe COVID-19, irrespective of immunosuppression status. NLR on day 1 >5.06 and day 4 >6.40 (p < 0.001), as well as PLR on day 1 >262.2 and day 4 >217.3 (p = 0.003), were associated with a greater probability for intubation. Similarly, a higher probability for death was found in the subset of patients with NLR on day 1 >4.82 (p < 0.001) and day 4 >6.41 (p < 0.001) and PLR on day 1 >229 (p = 0.009) and day 4 >205.4 (p = 0.003). Both PLR and NLR exhibited consistently higher negative predictive values (NPVs) (>93%) compared to positive predictive values (PPVs) for intubation and death. NLR and PLR displayed strong prognostic potential in hospitalized COVID-19 patients regarding intubation and death, irrespective of immunosuppression status, thus the surveillance of these biomarkers may help clinicians identify high-risk COVID-19 patients at an early stage.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; death; immunosuppression; intubation; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR); platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR); prognostic marker.
Conflict of interest statement
G.P. received speaker’s honoraria and consultancy from AstraZeneca, Gilead, GSK, Menarini, MSD, Norma, SOBI, and Pfizer, and research grants from University College London, Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis, Adagio Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bausch, Fabentech, Pfizer, PharmaMar, Roche, and Xenothera.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

