Human Papillomavirus-Encoded microRNAs as Regulators of Human Gene Expression in Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Transcriptomics Study
- PMID: 40559621
- PMCID: PMC12196474
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna11030043
Human Papillomavirus-Encoded microRNAs as Regulators of Human Gene Expression in Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Transcriptomics Study
Abstract
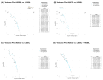
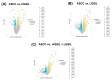
Introduction: Anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC) is a rare but increasingly common gastrointestinal malignancy, mainly associated with oncogenic human papillomaviruses (HPVs). The role of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in tumorigenesis is recognized, but the impact of viral ncRNAs on host gene expression remains unclear. Methods: We re-analyzed total RNA-Seq data from 70 anal biopsies: 31 low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LGSIL), 16 high-grade SIL (HGSIL), and 23 ASCC cases. Microbial composition was assessed taxonomically. Novel viral miRNAs were predicted using vsRNAfinder and linked to host targets using TargetScan and expression correlation analyses. Results: Microbial profiling revealed significant differences in abundance, with Alphapapillomaviruses types 9, 10, and 14 enriched across lesion grades. We identified 90 novel viral miRNAs and 177 significant anti-correlated miRNA-mRNA interactions. Target genes were enriched in pathways related to cell cycle, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, lipid metabolism, immune modulation, and viral replication. Discussion: Our findings suggest that HPV-derived miRNAs, including those from low-risk types, may contribute to neoplastic transformation by modulating host regulatory networks. Conclusion: This study highlights viral miRNAs as potential drivers of HPV-related anal cancer and supports their utility as early biomarkers and therapeutic targets in ASCC.
Keywords: anal squamous cell carcinoma; de novo miRNAs; human papillomavirus; oncomiR; squamous intraepithelial lesion; target prediction; transcriptomics; viral miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A MicroRNA Screen Identifies the Wnt Signaling Pathway as a Regulator of the Interferon Response during Flavivirus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02388-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28148804 Free PMC article.
-
Medical and surgical interventions for the treatment of usual-type vulval intraepithelial neoplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 5;2016(1):CD011837. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011837.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26728940 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as biomarkers in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review of recent clinical evidence.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022 Feb;213:107130. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107130. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35066247
-
Sun protection for preventing basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 25;7(7):CD011161. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011161.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27455163 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic vaccination against human papillomaviruses to prevent cervical cancer and its precursors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 9;5(5):CD009069. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009069.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29740819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The expanding world of noncoding RNA biology. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022;24:1447. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

