Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies
- PMID: 40559636
- PMCID: PMC12194312
- DOI: 10.3390/md23060227
Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies
Abstract
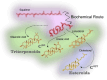
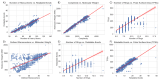
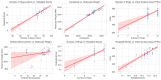
The expanding field of nutraceuticals and functional food science is increasingly turning to marine-derived bioactive compounds, particularly saponins, for their diverse pharmacological properties. These so-called thalassochemicals display distinctive structural features-such as sulfated glycosidic moieties and amphiphilic backbones-that underpin potent antitumor, hypolipidemic, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities. In contrast to their terrestrial analogs, marine saponins remain underexplored, and their complexity poses analytical and functional challenges. This review provides a critical and integrative synthesis of recent advances in the structural elucidation, biological function, and technological application of marine saponins. Special emphasis is placed on the unresolved limitations in their isolation, characterization, and structural validation, including coelution of isomers, adduct formation in MS spectra, and lack of orthogonal techniques such as NMR or FTIR. We illustrate these limitations through original MS/MS data and propose experimental workflows to improve compound purity and identification fidelity. In addition to discussing known structure-activity relationships (SARs) and mechanisms of action, we extend the scope by integrating recent developments in computational modeling, including machine learning, molecular descriptors, and quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models. These tools offer new avenues for predicting saponin bioactivity, despite current limitations in available high-quality datasets. Furthermore, we include a classification and comparison of steroidal and triterpenoid saponins from marine versus terrestrial sources, complemented by detailed chemical schematics. We also address the impact of processing techniques, delivery systems, and bioavailability enhancements using encapsulation and nanocarriers. Finally, this review contextualizes these findings within the regulatory and sustainability frameworks that shape the future of saponin commercialization. By bridging analytical chemistry, computational biology, and food technology, this work establishes a roadmap for the targeted development of marine saponins as next-generation nutraceuticals and functional food ingredients.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; food technology; marine biomaterials; nutraceuticals; saponins; thalassochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advances in antitumor activity and mechanism of natural steroidal saponins: A review of advances, challenges, and future prospects.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jun;128:155432. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155432. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38518645
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Marine-Derived Antioxidants: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential in Oxidative Stress-Associated Diseases.Mar Drugs. 2025 May 22;23(6):223. doi: 10.3390/md23060223. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40559632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Jolly A., Kim H., Moon J.Y., Mohan A., Lee Y.C. Exploring the imminent trends of saponins in personal care product development: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023;205:117489. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117489. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

