Advances in Jellyfish Sting Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies
- PMID: 40559640
- PMCID: PMC12194369
- DOI: 10.3390/md23060231
Advances in Jellyfish Sting Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies
Abstract
Jellyfish stings, as one of the most prevalent forms of marine injury, have increasingly become a subject of concern. Despite their simple morphology and structure, jellyfish possess a complex venom composition that can inflict varying degrees of damage on multiple human physiological systems. Consequently, the clinical symptoms associated with jellyfish stings are highly intricate. Although antivenoms have been developed for certain jellyfish species (e.g., C. fleckeri), specific antivenoms targeting the mechanisms of most jellyfish venoms remain understudied. To effectively prevent, treat, and cure jellyfish stings, we adhere to the principle of knowing their nature and their reasons. It is essential to investigate the emission mechanism of jellyfish nematocysts and the composition of their venom. Understanding these factors is crucial for the development of targeted treatment strategies. This review delves into the venom emission mechanism of jellyfish stinging cells, the symptoms resulting from jellyfish stings, and the comprehensive treatment strategies post-sting. It offers a scientific reference for comprehending jellyfish stings and establishes a theoretical foundation for subsequent research endeavors.
Keywords: biological activity; emission mechanism; jellyfish stings; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
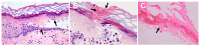



Similar articles
-
Interventions for the symptoms and signs resulting from jellyfish stings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 5;6(6):CD009688. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009688.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37272501 Free PMC article.
-
Biodiversity of jellyfish in the Indian coastal Ecosystem: Structural diversity, functional ecology, and venom dynamics with global implications.Mar Environ Res. 2025 Oct;211:107405. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2025.107405. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Mar Environ Res. 2025. PMID: 40752083 Review.
-
Investigation of Best Practices for Venom Toxin Purification in Jellyfish towards Functional Characterisation.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;15(3):170. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030170. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977061 Free PMC article.
-
The toxicity of Physalia physalis: systematic review and experimental study.Int Marit Health. 2025;76(1):42-62. doi: 10.5603/imh.101435. Int Marit Health. 2025. PMID: 40248951
-
Venom immunotherapy for preventing allergic reactions to insect stings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10(10):CD008838. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008838.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23076950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang C., Lyu Z., Wu J., Cheng C., Wang Y., Liu Z., Du B., Yang Y., Li F., Chen Q. Epidemiological analysis of jellyfish stings in coastal bathing beaches in Qinhuangdao City from 2017 to 2019. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021;33:593–595. - PubMed
-
- Lotan T. Leveraging Nematocysts Toward Human Care. Springer Nature Link; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2016. pp. 683–690.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

