StingReady: A Novel Device for Controlled Insect Sting Challenge-From Field Capture to Clinical Application
- PMID: 40559838
- PMCID: PMC12197535
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins17060260
StingReady: A Novel Device for Controlled Insect Sting Challenge-From Field Capture to Clinical Application
Abstract
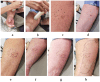
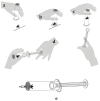
Reliable assessment of protection in venom immunotherapy (VIT) patients remains a clinical challenge, especially due to the limitations of conventional sting challenge tests (SCTs), which require complex insect handling and may compromise test accuracy. This study introduces StingReady, a novel, user-friendly device designed to streamline the SCT process by enabling safe, efficient, and minimally manipulative exposure to hymenopteran stings. For the first time, StingReady was applied to conduct SCTs with Vespa velutina, an invasive hornet species of increasing clinical relevance. The device was tested in a real-world setting at Belvís Park in Santiago de Compostela, Spain, where hornets were successfully captured and transported to the hospital without anesthesia or limb removal. The design features adjustable mesh sizes, allowing compatibility with various hymenopteran taxa. Using StingReady, nine patients underwent SCTs with no need for direct insect handling during the hospital procedure. The process improved patient safety and comfort while preserving the insect's natural stinging behavior, thereby enhancing test reliability. This study demonstrates that StingReady significantly improves SCT methodology, offering a practical, reproducible, and ethically sound alternative for evaluating VIT efficacy across diverse hymenopteran species.
Keywords: Vespa velutina; allergy testing; hymenoptera; insect handling; medical device; sting challenge; venom immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Venom immunotherapy for preventing allergic reactions to insect stings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10(10):CD008838. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008838.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23076950 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of Pharmalgen® for the treatment of bee and wasp venom allergy.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(12):III-IV, 1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta16120. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 22409877 Free PMC article.
-
Venom allergen immunotherapy in children: Short-term efficacy and impact on quality of life.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025 Aug;135(2):211-217.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2025.02.018. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40032206
-
Characteristics of Patients with Anaphylaxis to European Hornet (Vespa crabro) Venom Compared to Anaphylaxis to Wasp (Vespula spp.) Venom in Southern Germany.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025;186(7):652-661. doi: 10.1159/000542248. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39602896
-
Clinical Management of Wasp Stings Using Large Language Models: Cross-Sectional Evaluation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 4;27:e67489. doi: 10.2196/67489. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40466102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armisén M., Guspi R., Alfaya T., Cruz S., Fernández S., Domínguez-Noche C., Alonso A., Dalmau G., Marqués L., Vega A. Cross-Sectional Validation of a Quality of Life Questionnaire in Spanish for Patients Allergic to Hymenoptera Venom. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2015;25:176–182. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

