CYP1B1 Knockout in a Bovine Hepatocyte-like Cell Line (BFH12) Unveils Its Role in Liver Homeostasis and Aflatoxin B1-Induced Hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 40559872
- PMCID: PMC12197428
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins17060294
CYP1B1 Knockout in a Bovine Hepatocyte-like Cell Line (BFH12) Unveils Its Role in Liver Homeostasis and Aflatoxin B1-Induced Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
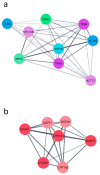
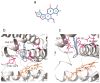
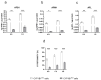
CYP1B1 is a key enzyme involved in xenobiotic and endogenous metabolism, yet its physiological role in bovine liver homeostasis remains unclear. In this study, we generated a CYP1B1 knockout (CYP1B1KO) bovine hepatocyte-like cell line to indirectly investigate its role in liver function. Transcriptomic analysis revealed alterations in immune regulation, epithelial barrier integrity, and detoxification pathways, with concurrent compensatory CYP1A1 upregulation. Beyond its physiological role, CYP1B1 was found to actively participate in Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) metabolism, a mycotoxin posing significant health risks to humans and livestock. Molecular docking suggested that CYP1B1 facilitates the conversion of AFB1 into AFM1 and AFBO. In agreement with these predictions, CYP1B1KO cells exposed to AFB1 showed reduced AFM1 production and decreased cytotoxicity. Further transcriptomic analysis indicated that CYP1B1KO cells exhibited mitigated oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, along with downregulation of CYP3A74, a key enzyme in AFB1 bioactivation. This suggests that CYP1B1 KO reduces AFB1 toxicity by directly limiting AFB1 bioactivation and indirectly modulating the broader hepatic CYP network, further limiting the formation of toxic intermediates. These findings provide novel insights into CYP1B1's function in bovine hepatocytes, highlighting its dual role in maintaining liver homeostasis and mediating AFB1 metabolism. The observed interplay between CYP1B1, CYP1A1, and CYP3A74 underscores the complexity of AFB1 biotransformation and warrants further investigation into the coordinated regulation of xenobiotic metabolism in cattle.
Keywords: AFB1; CRISPR/Cas9; CYP1B1; bovine; liver; molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shimada T., Hayes C.L., Yamazaki H., Amin S., Hecht S.S., Guengerich F.P., Sutter T.R. Activation of chemically diverse procarcinogens by human cytochrome P-450 1B1. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2979–2984. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

