Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, China: A Specific Investigation in Water-Scarce and Human Activity-Intensive Regions
- PMID: 40559895
- PMCID: PMC12196876
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13060422
Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, China: A Specific Investigation in Water-Scarce and Human Activity-Intensive Regions
Abstract
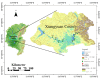
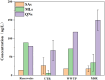
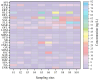
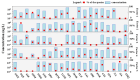
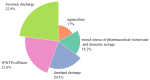
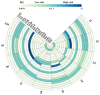
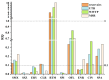
Antibiotic contamination and its environmental impact in water-scarce and human activity-intensive regions have been poorly researched, particularly in the Zhuozhang River, China. Thus, this study investigated the occurrence, sources, and ecological risks of 27 different antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, based on water samples collected from representative locations including major reservoirs, upstream of the river, the main river channel, and a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Results showed widespread contamination by quinolones, with concentrations ranged from 41.7 to 184.3 ng/L. Quinolones-particularly ofloxacin and cinoxacin-were identified as posing moderate ecological risks, with heightened concerns in the main river channel and wastewater treatment plant areas. Source apportionment using the positive matrix factorization model identified livestock farming as the dominant contributor to antibiotic pollution, accounting for 22.9% of the total antibiotic load in the river. These findings underscore the urgency of enhancing monitoring and management strategies to mitigate antibiotic contamination, especially in high-risk areas such as wastewater treatment plants and main river sections.
Keywords: Zhuozhang River; antibiotics; risk assessment; source apportionment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modelling antibiotics in a densely populated reservoir catchment: insights from Cirata Reservoir, Indonesia.Environ Pollut. 2025 Sep 15;381:126583. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126583. Epub 2025 May 31. Environ Pollut. 2025. PMID: 40456305
-
Applying the water quality indices, geographical information system, and advanced decision-making techniques to assess the suitability of surface water for drinking purposes in Brahmani River Basin (BRB), Odisha.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 May;32(23):13638-13673. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36329-z. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40164907
-
Prophylactic antibiotics for adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 15;1(1):CD013198. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013198.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33448349 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
Grants and funding
- U23A20157/the Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China Joint Fund for Regional Innovation and Development
- 42476266/National Science Foundation of China
- 202304041101020/Science and Technology Cooperation and Exchange Special Project of Shanxi Province
- X.J. Sun, 2024/the program for Young Scholar Grant of Wenying in Shanxi University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

