Integrative Spatial Proteomics and Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Unveil Molecular Complexity in Rheumatoid Arthritis for Novel Therapeutic Targeting
- PMID: 40559990
- PMCID: PMC12196869
- DOI: 10.3390/proteomes13020017
Integrative Spatial Proteomics and Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Unveil Molecular Complexity in Rheumatoid Arthritis for Novel Therapeutic Targeting
Abstract
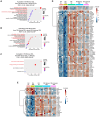
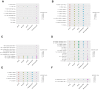
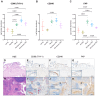
Understanding the heterogeneity of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and identifying therapeutic targets remain challenging using traditional bulk transcriptomics alone, as it lacks the spatial and protein-level resolution needed to fully capture disease and tissue complexities. In this study, we applied Laser Capture Microdissection (LCM) coupled with mass spectrometry-based proteomics to analyze histopathological niches of the RA synovium, enabling the identification of protein expression profiles of the diseased synovial lining and sublining microenvironments compared to their healthy counterparts. In this respect, key pathogenetic RA proteins like membrane proteins (TYROBP, AOC3, SLC16A3, TCIRG1, and NCEH1), and extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins (PLOD2, OGN, and LUM) showed different expression patterns in diseased synovium compartments. To enhance our understanding of cellular dynamics within the dissected regions, we further integrated the proteomic dataset with single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), and deduced cell type enrichment, including T cells, fibroblasts, NK cells, myeloid cells, B cells, and synovial endothelial cells. By combining high-resolution spatial proteomics and transcriptomic analyses, we provide novel insights into the molecular mechanisms driving RA, and highlight potential protein targets for therapeutic intervention. This integrative approach offers a more comprehensive view of RA synovial pathology, and mitigates the limitations of traditional bulk transcriptomics in target discovery.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; laser capture microdissection; mass spectrometry; membrane proteins; multi-omics integration; rheumatoid arthritis; scRNA-seq; untargeted proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employed by the AbbVie company. AbbVie funded the study and participated in study design, research, data collection, analysis and interpretation of data, writing, reviewing, and approving the publication. There are no additional conflicts of interest to report.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mass Spectrometry With Data-Independent Acquisition for the Identification of Target Antigens in Membranous Nephropathy.Am J Kidney Dis. 2025 Jul;86(1):63-73.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2025.01.014. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Am J Kidney Dis. 2025. PMID: 40058725
-
Spatial mapping of rheumatoid arthritis synovial niches reveals a LYVE1+ macrophage network associated with response to therapy.Ann Rheum Dis. 2025 Aug 22:S0003-4967(25)04292-X. doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.07.019. Online ahead of print. Ann Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 40849271
-
Integrative Proteomics and N-Glycoproteomics Analyses of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovium Reveal Immune-Associated Glycopeptides.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023 May;22(5):100540. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100540. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37019382 Free PMC article.
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis unsuccessfully treated with biologics: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 10;3(3):CD012591. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012591. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28282491 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
References
-
- Nakajima S., Tsuchiya H., Ota M., Ogawa M., Yamada S., Yoshida R., Maeda J., Shirai H., Kasai T., Hirose J., et al. Synovial Tissue Heterogeneity in Japanese Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Elucidated Using a Cell-Type Deconvolution Approach. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75:2130–2136. doi: 10.1002/art.42642. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Velickovic M., Fillmore T.L., Attah I.K., Posso C., Pino J.C., Zhao R., Williams S.M., Velickovic D., Jacobs J.M., Burnum-Johnson K.E., et al. Coupling Microdroplet-Based Sample Preparation, Multiplexed Isobaric Labeling, and Nanoflow Peptide Fractionation for Deep Proteome Profiling of the Tissue Microenvironment. Anal. Chem. 2024;96:12973–12982. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c00523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

