Transcriptomic sequencing and expression verification of identified genes modulating the alkali stress tolerance and endogenous photosynthetic activities of industrial hemp plant
- PMID: 40560904
- PMCID: PMC12194151
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326434
Transcriptomic sequencing and expression verification of identified genes modulating the alkali stress tolerance and endogenous photosynthetic activities of industrial hemp plant
Abstract
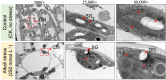
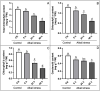
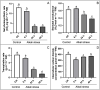
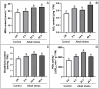
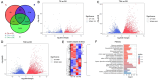
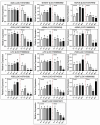
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) has a long cultivation history around the world. In northeast part of China, the alkaline soil geology severely reduces crop production. In this study, we tried to evaluate the impacts of alkali-induced stress on the photosynthetic status and physiological indices of hemp plants. The microscopic evaluation of endogenous ultrastructure clearly demonstrated significant oxidative damage to the structure of the photosynthetic tissues associated with the membrane, resulting from an increase in the levels of MGDG and DGDG. The deformed photosynthetic apparatus induced by alkali-stress significantly inhibited the biosynthesis process of photosynthetic pigments, causing 49.25%, 52.72%, 65.31%, and 28.13% loss in total Chl, Chl a, Chl b, and carotenoids, respectively. Meanwhile, the reduction in chlorophyll fluorescence parameters (Pn (74.62%), Gs (39.69%), and Tr (83.77%)) along with the obviously increased MDA (28.57%) and H2O2 (35.18%) content exhibited that the inhibitory effect of alkali-stress not only decreased the photosynthetic efficiency by intercepting the nutrient supply but also generated excessive ROS, resulting in oxidative stress. Transcriptomic analysis (RNA-sequencing) revealed the considerably enriched GO terms as well as KEGG pathways that exposed the significant DEGs. The qPCR expression evaluation of down-regulated chlorophyll biosynthesis-related major genes (GOGAT (LOC115699366) and HEMA (LOC133032634)) and photosystem-related major genes (PSB (LOC115701338) and HCF (LOC115707994)) exhibited important molecular evidence for modulating the photosynthesis activity of hemp plant under devastating mechanism of alkali-stress. However, the transcript patterns of photorespiration-related genes (GOX (LOC115697365) and GDC (LOC115707082)) showed a slower decreasing trend at late stress stage (at 24 ~ 48 h), and the transcription of SGAT gene (LOC115699360) was even enhanced by stress treatment at 48 h, probably in an attempt to adjust cellular carbon balance and elevate the antioxidant properties induced by alkali-stress.
Copyright: © 2025 Jiang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Physiological Mechanisms and Core Genes in Response to Saline-Alkali Stress in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.).Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 12;15(6):859. doi: 10.3390/biom15060859. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563499 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor CbbHLH147 improves alkali stress tolerance of Cinnamomun bodinieri by regulating flavonoid metabolism.Gene. 2025 Sep 10;964:149629. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2025.149629. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Gene. 2025. PMID: 40543688
-
Effects of cadmium (Cd) on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in the ornamental Plant Salvia splendens Ker-Gawl.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025 Mar;31(3):507-519. doi: 10.1007/s12298-025-01584-4. Epub 2025 Apr 6. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025. PMID: 40256272
-
Promotion of Ca2+ Accumulation in Roots by Exogenous Brassinosteroids as a Key Mechanism for Their Enhancement of Plant Salt Tolerance: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 9;24(22):16123. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216123. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003311 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to prevent occupational noise-induced hearing loss.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 7;7(7):CD006396. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006396.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28685503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qiao K, Takano T, Liu S. Discovery of two novel highly tolerant NaHCO3 trebouxiophytes: identification and characterization of microalgae from extreme saline–alkali soil. Algal Res. 2015;9:245–53. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2015.03.023 - DOI
-
- Li N, Cao BL, Chen ZJ, Xu K. Root morphology ion absorption and antioxidative defense system of two Chinese cabbage cultivars (Brassica rapa L.) reveal the different adaptation mechanisms to salt and alkali stress. Protoplasma 2022;259:385–98. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

