Seeding amplification assay with Universal Control Fluid: Standardized detection of α-synucleinopathies
- PMID: 40561143
- PMCID: PMC12194165
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326568
Seeding amplification assay with Universal Control Fluid: Standardized detection of α-synucleinopathies
Abstract
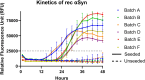
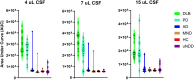
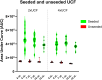
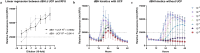
Seeding amplification assays, specifically the Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion method (RT-QuIC), have shown great diagnostic potential for α-synucleinopathies. Numerous research groups have demonstrated the method's high sensitivity and specificity using cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples and various RT-QuIC workflows. However, establishing a uniform and stably performing RT-QuIC protocol remains challenging. To address this, we established an RT-QuIC protocol with a Universal Control Fluid (UCF), which is simple to adopt, performs stably, and allows uniform preparation of both sample and control reactions. Firstly, we adapted and established a published 48-hour RT-QuIC protocol, including the in-house production of recombinant α-synuclein (rec α-syn), and evaluated its sensitivity and specificity through a blinded screening of an 81 CSF sample cohort consisting of Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), Alzheimer's disease, motor neuron disease, multiple system atrophy, unidentified neurodegenerative diseases, and healthy controls. Additionally, we tested all CSF samples in three volumes to determine which volume provides the best diagnostic accuracy. The established RT-QuIC performs nearly equally well with 7 µL and 15 µL added CSF, resulting in 94% and 94.5% diagnostic accuracy, respectively. Secondly, we developed a UCF solution and tested its performance with the established RT-QuIC protocol. Results indicate that UCF, used in defined volume and concentration, standardizes the preparation of both sample and control reactions without compromising the assay's diagnostic accuracy and provides a stabilizing environment for the reactions, ensuring higher reproducibility. The established RT-QuIC protocol for pathologic α-synuclein detection in PD and DLB CSF samples is highly sensitive (92-96%) and specific (93-96%). Therefore, it is important that its adoption in clinical laboratories is uncomplicated and uniform. RT-QuIC with UCF simplifies, standardizes, and stabilizes the assay's performance and, thus, could be recommended as a standard protocol for accurate detection of α-synucleinopathies.
Copyright: © 2025 Bsoul et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
KSF serves as consultant and/or member of an advisory board for Novo Nordisk, Eisai/Bioarctic, Eli Lilly, Roche Diagnostics (Remuneration paid to institution) , serves (or has served) as Principal or Sub-investigator and National Coordinator on several industry-sponsored phase 2 and 3 trials (indication Alzheimer´s disease): Roche, Roche Diagnostics, Biogen, NovoNordisk, Osuka, AbbVie (Remuneration paid to institution), serves on the Scientific advisory board (and as lecturer) on the MiCog educational program (supported by an unrestricted grant from Nestlé to the European Geriatric Medicines Society, personal remuneration), speaker and educational activities for Roche, Roche Diagnostics, Eisai/Bioarctic, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Lundbeck A/S (2023, 2024, 2025) (remuneration paid to institution), BestPractice Nordic, Alzheimerforeningen, Lundbeckfonden, Folkeuni-versitetet i Emdrup, Dagens medicin (2023, 2024, 2025) (Personal remuneration), serves as Editor-in-Chief for Alzheimer´s Research & Therapy Springer – Nature (from 2024 – 2023-2024 as Associate Editor) (Personal remuneration), receives royalties from publications with Springer-Nature and Hans Reitzels Forlag and has re-ceived funding or participated in research which has received funding from the following: Alzheimer Forsknings-fonden, Parkinsonforeningen, Aase og Ejner Danielsens Fond, KID fonden, Ellen Mørch Fonden, Jascha Fond-en, C2N, Overretssagfører L. Zeuthens Mindefond, Kong Christian den Tiendes Mindefond, Rigshospitalets Forskningspulje, Innovationsfonden, A.P. Møller fonden, ERA-PERMED, IHI, Hertzfonden, Harboefonden, Grosserer F.L.Foghts Fond, Fonden for Neurologisk Forskning, DANMODIS, Beckett fonden. Remaining authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Peelaerts W, Bousset L, Baekelandt V, Melki R. a-Synuclein strains and seeding in Parkinson’s disease, incidental Lewy body disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy: similarities and differences. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;373(1):195–212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

