Serum Autoantibody Titers and Neurofilament Light Chain Levels in CASPR2/LGI1 Encephalitis: A Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 40561419
- PMCID: PMC12202019
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200431
Serum Autoantibody Titers and Neurofilament Light Chain Levels in CASPR2/LGI1 Encephalitis: A Longitudinal Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Autoantibodies against contactin-associated protein-like 2 (CASPR2-IgG) and leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1 protein (LGI1-IgG) identify a subgroup of autoimmune encephalitis (AE). Up to 65% of patients with LGI1/CASPR2 AE show cognitive sequelae that are unpredictable at onset. We aimed to assess the clinical relevance of serum autoantibody titers and neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels as biomarkers in CASPR2/LGI1 AE.
Methods: We selected consecutive CASPR2/LGI1-IgG-positive patients with at least 2 longitudinal serum samples obtained more than 60 days apart. Samples were defined as acute (first diagnostic evaluation after onset or relapse and before immunotherapy) and remission (>2 months from attack). CASPR2/LGI1-IgG was titered with a live cell-based assay. Functional outcome was measured using modified Rankin Scale and Clinical Assessment Scale in AE and cognitive impairment using Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA).
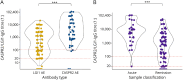
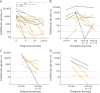
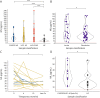
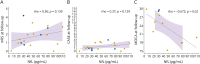
Results: We included 23 patients (LGI1 = 15, CASPR2 = 7, CASPR2/LGI1 = 1) with 130 serum samples (acute = 32; remission = 98). Serum titers in the acute phase were higher than in remission and decreased over time and after immunosuppressive treatment. In 9 of 10 patients, relapses occurred with seropositive samples, and in 4 of 5 patients, these occurred with increased titers. Onset titers did not correlate with functional/cognitive outcome at follow-up.Serum NfL median levels in both patients with LGI1 AE (35.3 pg/mL, range: 5.4-164) and CASPR2 AE (31.4 pg/mL, range: 9.11-120) were higher than in age/sex-matched controls (14.55, range: 5.4-56.8, p = 0.004 and p < 0.001, respectively). Acute-phase samples had higher NfL median levels (47.2, range: 9.11-120) compared with remission (31.2 pg/mL; range, 5.4-114, p = 0.02). NfL levels at onset predicted lower MoCA scores at follow-up in univariate linear regression analysis (B = -3.881, p = 0.0256). NfL levels decreased over time, but at the last follow-up remained higher than those in controls (p = 0.02).
Discussion: Measuring LGI1 and CASPR2-IgG titers in AE could help to confirm the disease stage and define relapses but has no prognostic implications. Serum NfL at onset could be used to identify patients at higher risk of cognitive sequelae that might deserve tailored management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Full disclosure form information provided by the authors is available with the full text of this article at
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
