Cycle versus swap strategy after TNFi discontinuation in psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis: a quasi-experimental study
- PMID: 40562682
- PMCID: PMC12198808
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005566
Cycle versus swap strategy after TNFi discontinuation in psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis: a quasi-experimental study
Abstract
Objectives: To compare a bDMARD mode of action cycle vs swap treatment strategy in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) or axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) after first tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) discontinuation.
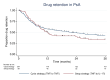
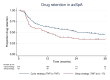
Methods: In December 2019, our local treatment protocol for PsA and axSpA changed from a cycle strategy (first TNFi to second TNFi) to a swap strategy (first TNFi to IL-17i). We performed a retrospective comparison of the 3-year drug retention rate using multivariable Cox regression (ref: cycle group) and disease activity (DAS28-CRP for PsA, BASDAI for axSpA) in patients with a clinical diagnosis of PsA and axSpA. For subgroup analyses, Cox regression models were stratified by sex, reason of first TNFi discontinuation, and (non-)radiographic status in axSpA.
Results: In PsA patients (n=406), there was no overall significant difference in drug retention between strategies (HR: 1.17 (95% CI: 0.87 to 1.58), p=0.29), but male PsA patients had a significant higher risk for treatment discontinuation following a swap strategy. In axSpA patients (n=335), the swap strategy was overall associated with a higher risk of treatment discontinuation (HR: 1.46 (95% CI: 1.03 to 2.07), p=0.04). Patients who discontinued their first TNFi due to inefficacy and patients diagnosed with radiographic axSpA were at significant higher risk for treatment discontinuation following a swap strategy. No significant differences in disease activity were found for treatment strategies in PsA or axSpA.
Conclusion: In PsA, the cycle and swap treatment strategy performed similarly, while in axSpA, the cycle strategy was associated with a significant higher drug retention rate.
Keywords: Arthritis, Psoriatic; Axial Spondyloarthritis; Interleukin-17; Treatment; Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: IvE: None declared, JEV: Received grants from Novartis and Eli Lilly, unrelated to the current study, NdB: None declared, LdB: None declared, AAdB: Received grants for research and quality of care projects to the institution from Lilly, Abbvie, Galapagos, Novartis, Pfizer, Gilead, Sanofi, Biogen and Celltrion, unrelated to the current study, NvH: None declared, EM: Received grants for research and quality of care projects to the institution from Abbvie, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Novartis, unrelated to the current study, EFAL: Received funding for research grants from Novartis and Eli Lilly, unrelated to the current study.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
