Disseminated Histoplasmosis in Persons Living with HIV, France and Overseas Territories,1992-2021
- PMID: 40562731
- PMCID: PMC12205452
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3107.241931
Disseminated Histoplasmosis in Persons Living with HIV, France and Overseas Territories,1992-2021
Abstract
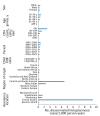
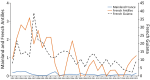
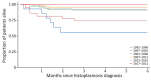
Disseminated histoplasmosis is a major issue among persons with advanced HIV in the Americas; it might also affect persons in sub-Saharan Africa, the Caribbean, and Asia and can be mistaken for other infections. By using 1992-2021 data from the French hospital database on HIV, we analyzed 198,798 persons with HIV follow-up in France and its overseas territories, identifying 553 (2.8/1,000 person-years) first episodes of disseminated histoplasmosis. Incidence rates varied by site of follow-up: 9.41 in French Guiana, 0.76 in Guadeloupe, 0.62 in Martinique, and 0.079 in mainland France. Incidence rates in France also varied between regions of origin or travel: 4.73 for Central or South America, 1.36 for the Caribbean, and 0.19 for sub-Saharan Africa or Asia. Differences persisted after adjusting for age, sex, CD4 count, and viral load at baseline. Overall, incidence and early death have declined, likely because of antiretroviral drug rollout in France.
Keywords: Africa; Americas; Asia; Caribbean; France; HIV/AIDS and other retroviruses; Histoplasma spp.; fungal infection; fungi; global burden; histoplasmosis; incidence.
Figures
References
-
- Samayoa B, Roy M, Cleveland AA, Medina N, Lau-Bonilla D, Scheel CM, et al. High mortality and coinfection in a prospective cohort of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients with histoplasmosis in Guatemala. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;97:42–8. 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Falci DR, Monteiro AA, Braz Caurio CF, Magalhães TCO, Xavier MO, Basso RP, et al. Histoplasmosis, an underdiagnosed disease affecting people living with HIV/AIDS in Brazil: results of a multicenter prospective cohort study using both classical mycology tests and histoplasma urine antigen detection. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6:ofz073. 10.1093/ofid/ofz073 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

