Polyglutamylation of microtubules drives neuronal remodeling
- PMID: 40562742
- PMCID: PMC12198417
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60855-6
Polyglutamylation of microtubules drives neuronal remodeling
Abstract
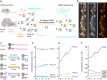
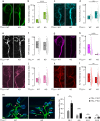
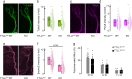
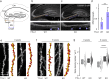
Developmental remodeling shapes neural circuits via activity-dependent pruning of synapses and axons. Regulation of the cytoskeleton is critical for this process, as microtubule loss via enzymatic severing is an early step of pruning across many circuits and species. However, how microtubule-severing enzymes, such as spastin, are activated in specific neuronal compartments remains unknown. Here, we reveal that polyglutamylation, a post-translational tubulin modification enriched in neurons, plays an instructive role in developmental remodeling by tagging microtubules for severing. Motor neuron-specific gene deletion of enzymes that add or remove tubulin polyglutamylation-TTLL glutamylases vs. CCP deglutamylases-accelerates or delays neuromuscular synapse remodeling in a neurotransmission-dependent manner. This mechanism is not specific to peripheral synapses but also operates in central circuits, e.g., the hippocampus. Thus, tubulin polyglutamylation acts as a cytoskeletal rheostat of remodeling that shapes neuronal morphology and connectivity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Burute, M. & Kapitein, L. C. Cellular logistics: Unraveling the interplay between microtubule organization and intracellular transport. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol.35, 29–54 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Gudimchuk, N. B. & McIntosh, J. R. Regulation of microtubule dynamics, mechanics and function through the growing tip. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.22, 777–795 (2021). - PubMed
-
- McKenna, E. D., Sarbanes, S. L., Cummings, S. W. & Roll-Mecak, A. The tubulin code, from molecules to health and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol.39, 331–361 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Janke, C. & Magiera, M. M. The tubulin code and its role in controlling microtubule properties and functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.21, 307–326 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 390857198/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 450131873/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 403584255/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 523862973/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 390857198/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 428663564/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 408885537/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 2023/Association France Alzheimer (French Alzheimer's Association)
- CNATM/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)
- ANR-17-CE13-0021/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-20-CE13-0011/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- FP/2007-2013; 616791/EC | EC Seventh Framework Programm | FP7 Ideas: European Research Council (FP7-IDEAS-ERC - Specific Programme: "Ideas" Implementing the Seventh Framework Programme of the European Community for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities (2007 to 2013))
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

