The mitochondrial methylation potential gates mitoribosome assembly
- PMID: 40562754
- PMCID: PMC12198368
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60977-x
The mitochondrial methylation potential gates mitoribosome assembly
Abstract
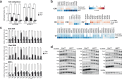
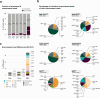
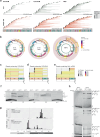
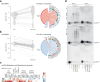
S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is the principal methyl donor in cells and is essential for mitochondrial gene expression, influencing RNA modifications, translation, and ribosome biogenesis. Using direct long-read RNA sequencing in mouse tissues and embryonic fibroblasts, we show that processing of the mitochondrial ribosomal gene cluster fails in the absence of mitochondrial SAM, leading to an accumulation of unprocessed precursors. Proteomic analysis of ribosome fractions revealed these precursors associated with processing and assembly factors, indicating stalled biogenesis. Structural analysis by cryo-electron microscopy demonstrated that SAM-dependent methylation is required for peptidyl transferase centre formation during mitoribosome assembly. Our findings identify a critical role for SAM in coordinating mitoribosomal RNA processing and large subunit maturation, linking cellular methylation potential to mitochondrial translation capacity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Monné, M., Marobbio, C. M. T., Agrimi, G., Palmieri, L. & Palmieri, F. Mitochondrial transport and metabolism of the major methyl donor and versatile cofactor S‐adenosylmethionine, and related diseases: a review†. IUBMB Life74, 573–591 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- VR2022-01287, VR2023-07091/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)
- NN0082202/Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research (NovoNordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research)
- KAW2019.0109/Knut och Alice Wallenbergs Stiftelse (Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation)
- 2-190/2022/Karolinska Institutet (Karolinska Institute)
- 21 1621 Pj/Cancerfonden (Swedish Cancer Society)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

