Antioxidant Effect of a Fucus vesiculosus Extract on Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats: A Biochemical and Histological Study
- PMID: 40563259
- PMCID: PMC12189128
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14060624
Antioxidant Effect of a Fucus vesiculosus Extract on Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats: A Biochemical and Histological Study
Abstract
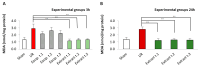
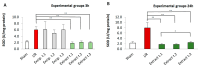
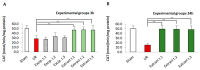
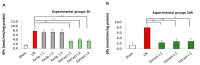
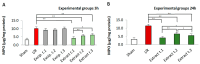
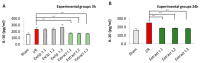
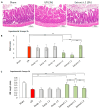
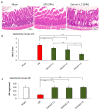
Fucus vesiculosus is a brown seaweed known for its strong antioxidant properties, mainly attributed to its high polyphenolic content. This study aimed to evaluate the antioxidant protective effect of an optimised F. vesiculosus extract in an experimental model of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, considering the intestine as particularly vulnerable to this pathology. Seventy-two male Wistar albino rats were randomly divided into twelve groups: Sham, I/R groups (3 and 24 h reperfusion), I/R plus vehicle groups (three application times, 3 h reperfusion), and I/R plus F. vesiculosus extract groups (three application times, 3 and 24 h reperfusion). Intestinal injury was assessed through biochemical markers (malondialdehyde [MDA], superoxide dismutase [SOD], catalase [CAT], glutathione peroxidase [GPx], and mieloperoxidase [MPO]), inflammatory cytokines (interleukin 1 β [IL-1β] and interleukin [IL-10]), and histological analysis. Results demonstrated that treatment with F. vesiculosus significantly reduced oxidative stress and inflammation caused by I/R injury (p < 0.05), restoring analysed parameters (MDA, SOD, CAT, IL-10) to levels comparable to the Sham group. Histological examination confirmed the preservation of intestinal mucosal integrity following F. vesiculosus administration. These findings suggest that the antioxidant extract from F. vesiculosus effectively protects against intestinal I/R injury, highlighting its potential for clinical use in preventing and managing this pathological condition, particularly in surgical contexts.
Keywords: Fucus vesiculosus; antioxidant; intestinal ischemia/reperfusion; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aranda-Rivera A.K., Cruz-Gregorio A., Arancibia-Hernández Y.L., Hernández-Cruz E.Y., Pedraza-Chaverri J. RONS and oxidative stress: An overview of basic concepts. Oxygen. 2022;2:437–478. doi: 10.3390/oxygen2040030. - DOI
-
- Namirah I., Wimbanu K.S., Rompies A.M.E., Prayogo Y.S., Arozal W., Fadilah, Hanafi M., Hardiany N.S. The effect of ethanol-based coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) seed extract on oxidative stress, antioxidant level and cellular senescence in the heart of obese rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2024;12:1111–1120. doi: 10.56499/jppres24.1957_12.6.1111. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

