Subcritical Water and Pressurised Ethanol Extractions for Maximum Recovery of Antioxidants from Orange Peel Herbal Dust with Evaluation of Its Pharmacological Potential Using In Silico and In Vitro Analysis
- PMID: 40563273
- PMCID: PMC12189749
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14060638
Subcritical Water and Pressurised Ethanol Extractions for Maximum Recovery of Antioxidants from Orange Peel Herbal Dust with Evaluation of Its Pharmacological Potential Using In Silico and In Vitro Analysis
Abstract
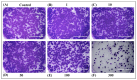
This research explored the potential of pressurised liquid extraction techniques for valorising herbal orange peel dust (OPD) waste from the filter tea industry. A series of experiments were conducted, varying the temperature (120-220 °C) and solvent (water and 50% (v/v) ethanol), while pressure and time were kept constant. Afterward, the obtained extracts were analysed by LC-ESI-MS/MS for determining the chemical composition. The highest concentrations of the most dominant compounds, the antioxidants hesperidin (662.82 ± 22.11 mg/L) and naringin (62.37 ± 2.05 mg/L), were found at specific temperatures using subcritical water extraction. In silico studies indicated that these compounds could interact with sirtuin-1 and growth factor beta receptors, suggesting potential anti-ageing benefits for skin. In vitro experiments on rat hepatoma cells (H4IIE) revealed that OPD extracts had antitumor potential, inhibiting cell proliferation and altering cell morphology. These findings underscore the importance of temperature and extraction technique in obtaining antioxidant-rich extracts with pharmacological potential. The resulting extracts, obtained using green solvents, show promise for cosmetic applications, though further in vivo studies are needed to confirm their therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: antitumor activity; orange peel herbal dust; pressurised ethanol extraction; pressurised liquid extraction; subcritical water extraction; waste valorisation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Pharmacotherapies for sleep disturbances in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 16;11(11):CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 15;11:CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub4. PMID: 27851868 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Colegate S.M., Molyneux R.J. Bioactive Natural Products: Detection, Isolation, and Structural Determination. 2nd ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2007.
-
- Vidović S., Vladić J., Nastić N., Jokić S. Subcritical and supercritical extraction in food by-product and food waste valorization. In: Muthukumarappan K., Knoerzer K., editors. Innovative Food Processing Technologies: A Comprehensive Review. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2021. pp. 705–721. - DOI
-
- Vidović S., Nastić N., Gavarić A., Cindrić M., Vladić J. Development of green extraction process to produce antioxidant-rich extracts from purple coneflower. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019;54:1174–1181. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2018.1527854. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

