Development of Value-Added Chicken Burgers by Adding Pumpkin Peel Powder as a Sustainable Ingredient
- PMID: 40563283
- PMCID: PMC12190050
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14060648
Development of Value-Added Chicken Burgers by Adding Pumpkin Peel Powder as a Sustainable Ingredient
Abstract
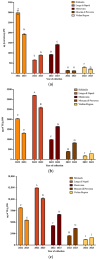
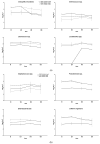
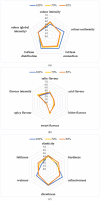
Worldwide, there is a growing need to valorize agri-food waste containing bioactive compounds to fit into the circular economy action plan approved in Europe. In this paper, the carotenoids of peel powder of pumpkins (PPP) of five varieties (Hokkaido, Lunga di Napoli, Mantovana, Moscata di Provenza, and Violina rugosa) were characterized by spectrophotometric (antioxidant activity) and chromatographic analyses. PPP from the Hokkaido variety showed high levels of carotenoids (2993.90 μg β-carotene equivalents/g). They were mainly composed of mono- (9065.35 μg zeaxanthin dipalmitate equivalents/g) and di-esterified (1832.74 μg zeaxanthin dipalmitate equivalents/g) xanthophylls. It also showed high antioxidant activity (ABTS 2036.02 μg Trolox equivalents/g). Therefore, it was used as a functional plant ingredient (4%) to prepare chicken burgers (100, 70, and 50% chicken meat). Physical-chemical, microbiological, color, and sensorial analyses of fortified chicken burgers were carried out. The product with 70% chicken meat and 4% PPP obtained the highest overall acceptability score (5.95 ± 0.25). The results confirm that the addition of PPP could represent a valid approach to increasing the health properties and acceptability of burgers, even if a larger assessor size is necessary.
Keywords: agri-food waste; carotenoids; fortified meat; microbiological assay; sensory analysis; ultrasound-assisted extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- EUROSTAT. 2025. [(accessed on 2 April 2025)]. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Food_....
-
- Singh K., Kumar T., Patel V., Kumar V., Sharma S., Pradesh Krishi Vishvavidyalaya H., Pradesh H., Jyoti Rani I., Kavindra Singh C., Rani J. A review on the conversion of food wastes and by-products into value added products. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019;7:2068–2073.
-
- Khalid W., Arshad M.S., Ranjha M.M.A.N., Rozanska M.B., Irfan S., Shafique B., Rahim M.A., Khalid M.Z., Abdi G., Kowalczewski P.Ł. Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders. Open Life Sci. 2022;17:1075–1093. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

