The DJ-1-Binding Compound Exerts a Protective Effect in Both In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 40563351
- PMCID: PMC12189621
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14060719
The DJ-1-Binding Compound Exerts a Protective Effect in Both In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
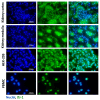
Although sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, its treatment remains unresolved. Oxidative stress and inflammation are key elements in the pathomechanism of AKI. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the role of DJ-1 protein, known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in an animal model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced AKI. The presence of DJ-1 was detected by immunofluorescence staining in mice kidney samples, human embryonic kidney cells (HEK-293), and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). To investigate DJ-1 functions, Compound-23, a specific DJ-1-binding and preserving compound (CAS: 724737-74-0), was used in vitro and in vivo. Compound-23 reduced the H2O2-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production of the HEK-293 cells, and their LPS- or H2O2-induced death, as well. In accordance, Compound-23 decreased the mRNA expression of the oxidative stress markers NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) and glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCLC) in the LPS-treated, and NQO1 in the H2O2-treated cells. Moreover, Compound-23 reduced the H2O2- and LPS-induced mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 (IL6) in both HEK-293 and PBMCs. Using the mice model of LPS-induced AKI, we demonstrated that Compound-23 treatment improved the renal functions of the mice. In addition, Compound-23 decreased the renal mRNA expression of kidney injury molecule 1 (Kim1), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (Ngal), Nqo1, Gclc, and Il6 in the LPS-treated mice. Our study revealed that compounds protecting DJ-1 functions may protect the kidney from LPS-induced damage, suggesting that DJ-1 could be a potential drug target for sepsis-induced AKI therapy.
Keywords: DJ-1; PARK7; acute kidney injury; antioxidant; drug development; inflammation; oxidative stress; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
- 02022/HUN-REN-SE Pediatric and Nephrology Research Group
- K-142728/National, Research, Development and Innovation Office (NKFIH)
- TKP2021-EGA-24/National, Research, Development and Innovation Office (NKFIH)
- EKÖP-2024-53/National, Research, Development and Innovation Office (NKFIH)
- EKÖP-2024-160/National, Research, Development and Innovation Office (NKFIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

