Blood Orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) Juice By-Product Extract as a Functional Feed Additive: Effects on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Status, Immune Parameters, and Disease Resistance Against Vibrio harveyi in Juvenile Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)
- PMID: 40563377
- PMCID: PMC12189218
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14060745
Blood Orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) Juice By-Product Extract as a Functional Feed Additive: Effects on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Status, Immune Parameters, and Disease Resistance Against Vibrio harveyi in Juvenile Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)
Abstract
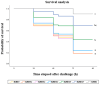
This study evaluated the antibacterial activity and residual functional compounds of blood orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) juice by-product extract (BJBE). The effects of dietary BJBE on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant status, immune parameters, and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi were examined in juvenile black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). In total, 630 juvenile rockfish were randomly assigned to 21 rectangular tanks (50 L) for a feeding trial, with 30 fish per tank in triplicate. Seven isonitrogenous and isolipidic experimental diets were formulated with BJBE at 0 (control, BJBE0), 0.1 (BJBE0.1), 0.2 (BJBE0.2), 0.3 (BJBE0.3), 0.5 (BJBE0.5), 0.7 (BJBE0.7), and 1.0 (BJBE1) g kg-1. A disk diffusion assay confirmed BJBE's strong antibacterial efficacy against V. harveyi. After an 8-week feeding trial, fish fed BJBE0.7 and BJBE1 exhibited significantly a greater final weight, weight gain, and specific growth rate compared with those fed BJBE0. Feed efficiency was significantly higher in fish fed BJBE0.7 than in those fed BJBE0. The protein efficiency ratio was significantly higher in fish fed BJBE0.3, BJBE0.5, BJBE0.7, and BJBE1 relative to those fed BJBE0. Intestinal amylase activity was significantly higher in fish fed BJBE0.7 and BJBE1 compared with those fed BJBE0, and trypsin activity was significantly higher in BJBE0.7-fed fish than in BJBE0-fed fish. In comparison to the BJBE0 diet, the plasma superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione levels of fish fed BJBE0.7 and BJBE1 diets were significantly higher. Lysozyme activity and immunoglobulin M level in fish fed BJBE0.7 and BJBE1 were significantly higher than that in fish fed BJBE0. After a challenge with V. harveyi, disease resistance was significantly higher in fish fed BJBE0.5, BJBE0.7, and BJBE1 compared with those fed BJBE0. Overall, 0.7-1.0 g kg-1 is proposed as the optimal dietary BJBE inclusion level for enhancing growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant status, immune parameters, and disease resistance against V. harveyi infection in juvenile black rockfish.
Keywords: Citrus sinensis; Sebastes schlegelii; by-products; disease resistance; growth performance; health status.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Toop T.A., Ward S., Oldfield T., Hull M., Kirby M.E., Theodorou M.K. AgroCycle–developing a circular economy in agriculture. Energy Procedia. 2017;123:76–80. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.07.269. - DOI
-
- Ladisa C., Bruni M., Lovatelli A. Overview of ornamental species aquaculture. FAO Aquac. Newsl. 2017;56:39.
-
- FAO . The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Sustainability in Action. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2020.
-
- Obi F., Ugwuishiwu B., Nwakaire J. Agricultural waste concept, generation. Utilization and management. Niger. J. Technol. 2016;35:957. doi: 10.4314/njt.v35i4.34. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

