Targeting Glioblastoma Stem Cells: A40s Aptamer-NIR-Dye Conjugate for Glioblastoma Visualization and Treatment
- PMID: 40563410
- PMCID: PMC12190191
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15060768
Targeting Glioblastoma Stem Cells: A40s Aptamer-NIR-Dye Conjugate for Glioblastoma Visualization and Treatment
Abstract
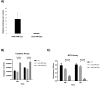
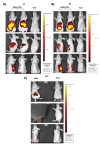
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most aggressive and challenging brain cancer, in terms of diagnosis and therapy. The highly infiltrative glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) are difficult to visualize and surgically remove with the current diagnostic tools, which often lead to misdiagnosis and false-positive results. In this study, we focused on a groundbreaking tool for specifically visualizing and removing GSCs. We exploited the specific binding of A40s aptamer to EphA2 for the selective delivery of Near-Infrared Dyes (NIR-Dyes), like IR700DX and ICG, both in vitro and in vivo. The A40s aptamer, engineered through the NIR-Dye conjugation, did not affect aptamer binding ability; indeed, A40s-NIR-Dye conjugates bound GLI261 stem-like cells and patient-derived GSCs in vitro; moreover, they induced cell death upon photodynamic therapy treatment (PDT). Additionally, when systemically administrated, the A40s-NIR-Dye conjugates allowed GSC visualization and accumulated in tumor mass. This allows GSCs detection and treatment. Our findings demonstrate the potential use of A40s aptamer as a targeted therapeutic approach and imaging tool in vivo for GSCs, paving the way for improved, more effective, and less invasive GBM management.
Keywords: A40s; EphA2; GBM; ICG; IR700DX; NIR dye; PDT; aptamers; glioblastoma stem cells; guide surgery; photodynamic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Alessandra Affinito, Sara Verde and Aurelia Fraticelli were employed by the company AKA Biotech. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sabouri M., Dogonchi A.F., Shafiei M., Tehrani D.S. Survival rate of patient with glioblastoma: A population-based study. Egypt. J. Neurosurg. 2024;39:42. doi: 10.1186/s41984-024-00294-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

