Role of Nutritional Elements in Skin Homeostasis: A Review
- PMID: 40563448
- PMCID: PMC12190690
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15060808
Role of Nutritional Elements in Skin Homeostasis: A Review
Abstract
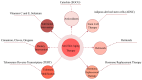
Skin aging is the most prominent phenotype of human aging and is the result from the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Improving skin aging is essential for maintaining the normal physiological function of the skin and the mental health of the human body. Existing studies have proposed many theories of aging, such as the free radical theory, mitochondrial theory of aging, etc., and accordingly have also proposed appropriate interventions. It is worth noting that many nutrients contained in the skin itself play an important role in maintaining skin health. During the aging process, a decrease in the levels of these nutrients is closely related to a weakening of the related functions. Therefore, supplementing these nutrients offers potential therapeutic options for improving skin aging. In this review, we summarize the important roles of nutrients in the skin and their potential in anti-aging, with the expectation of providing a therapeutic basis and clinical reference for delaying skin aging.
Keywords: aging; antioxidant; nutrient; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32402845/Chinese National Natural Science Foundation
- 5244041/Beijing Natural Science Foundation
- 2022R10260010/Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology Project
- XTCXGC2021012/Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences "5511" Collaborative Innovation Project
- 2024J01332/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

