Pre-Amplification of Cell-Free DNA: Balancing Amplification Errors with Enhanced Sensitivity
- PMID: 40563524
- PMCID: PMC12191314
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15060883
Pre-Amplification of Cell-Free DNA: Balancing Amplification Errors with Enhanced Sensitivity
Abstract
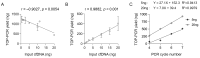
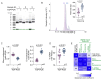
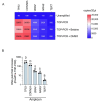
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) is a promising biomarker for personalised oncology. However, its clinical utility is limited by detection sensitivity, particularly in early-stage disease. T-Oligo Primed Polymerase Chain Reaction (TOP-PCR) is a commercial amplification approach utilising an efficient "half-adapter" ligation design and a single-primer-based PCR strategy. This study evaluated the clinical value and application of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) pre-amplification. cfDNA amplification with TOP-PCR preserved DNA size profiles and resulted in a 22 bp size increase due to the half-adaptor ligation. Gene target amplification rates varied, showing lower efficiency for the GC-rich TERT promoter amplicon and higher efficiency for the BRAF and TP53 amplicons. Optimised pre-amplification (20 ng cfDNA input and 5-7 cycles of PCR) enhanced ctDNA detection sensitivity and expanded sample availability for the detection of multiple tumour-informed mutations. Importantly, PCR errors emerged in pre-amplified cfDNA samples, underscoring the necessity for negative controls and the establishment of stringent mutation positivity thresholds.
Keywords: circulating tumour DNA; detection sensitivity; melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
J.H.L. received honorarium from MSD, BMS, Sanofi, Roche, AstraZeneca, and Novartis and sits of advisory boards for MSD, BMS, and Sanofi. R.A.S. has received fees for professional services from SkylineDx BV, IO Biotech ApS, MetaOptima Technology Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Evaxion, Provectus Biopharmaceuticals Australia, Qbiotics, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, NeraCare, AMGEN Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Myriad Genetics, and GlaxoSmithKline. G.V.L. is a consultant advisor for Agenus, Amgen, Array Biopharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BioNTech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Evaxion, Hexal AG (Sandoz Company), Highlight Therapeutics S.L., IOBiotech, Immunocore, Innovent Biologics USA, Merck Sharpe & Dohme, Novartis, PHMR Ltd., Pierre Fabre, Regeneron, Scancell, and SkylineDX B.V. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell-Free DNA in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Oncologist. 2017 Sep;22(9):1049-1055. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0178. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28778958 Free PMC article.
-
The evidence base for circulating tumour DNA blood-based biomarkers for the early detection of cancer: a systematic mapping review.BMC Cancer. 2017 Oct 23;17(1):697. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3693-7. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29061138 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemistry as a reliable method for detection of BRAF-V600E mutation in melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of current published literature.J Surg Res. 2016 Jun 15;203(2):407-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.04.029. Epub 2016 Apr 23. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27363650
-
Refined Procedure to Purify and Sequence Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 18;26(12):5839. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125839. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565311 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free epigenomes enhanced fragmentomics-based model for early detection of lung cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Feb;15(2):e70225. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70225. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39909829 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

