Cryoablation and Intratumoral Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer: A Future Path to Cost-Effective De-Escalation for Larger Tumors, Lymph Nodes and Metastatic Disease
- PMID: 40563565
- PMCID: PMC12190262
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17121915
Cryoablation and Intratumoral Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer: A Future Path to Cost-Effective De-Escalation for Larger Tumors, Lymph Nodes and Metastatic Disease
Abstract
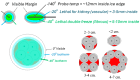
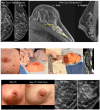
Cryoablation is a promising, cost-effective option to de-escalate surgical breast cancer morbidity, but presently is only suggested for breast cancers < 1.5 cm, in select candidates. Breast cancer cryoablation is not a reliably covered procedure by insurance and is mainly guided by ultrasound (US), using a single cryoprobe. Yet, cryoablation is an accepted treatment option for various malignancies, including those of the kidney, liver and lung, utilizing a predominantly CT-guided, multi-probe approach using crucial cytotoxic isotherms for thorough tumor coverage. Cryoablation thus continues to find new clinical utility and is rapidly advancing on multiple fronts, similar to immunotherapy. Clinical concerns of expanding cryoablation to breast tumors > 1.5 cm is more related to the greater risk of metastatic spread to local lymph nodes and beyond. Combined adjuvant treatment, such as radiation and/or chemotherapy, are currently used for regional and systemic breast cancer control, but have significant associated morbidities. US/CT-guided multi-probe large-volume breast cryoablation is presented as a thorough local control option for select patients. Intratumoral chemotherapy by direct tumor injection has been shown to be safe and is currently being tested with immunotherapy drugs and exhibits much lower morbidity. Cryoablation combined with intratumoral immunotherapy is presented to show robust systemic immune response and the potential to provide additional protection from regional and/or metastatic disease spread while de-escalating the morbidities from current adjuvant treatments for larger breast cancers. While further clinical trials are needed, it is essential to pursue safe and effective breast cancer treatments that offer the potential for cost-efficiency and therapeutic de-escalation across a wide spectrum of breast cancer cases.
Keywords: breast cancer; cryoablation; de-escalation; immunotherapy; intratumoral.
Conflict of interest statement
P.J.L. acknowledges that he served as Chief Medical Officer of Rampart Health, LLC and is a co-author of the abstract presented at the 2023 SITC conference referenced in this review. He also discloses his current role as Chief Medical Consultant for Delphinus Medical Technologies, Inc., the manufacturer of the SoftVue device. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Cancer Statistics for Breast Cancer. National Cancer Institute. [(accessed on 18 October 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

