Combined Radiation and Endocrine Therapies Elicit Benefit in ER+ Breast Cancer
- PMID: 40563571
- PMCID: PMC12190792
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17121921
Combined Radiation and Endocrine Therapies Elicit Benefit in ER+ Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Standard treatment for patients with early-stage estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer often includes sequential adjuvant radiation and endocrine therapies. Unfortunately, ~1/3 of patients eventually experience disease recurrence, partly due to residual disease in the form of drug-tolerant persister cancer cells. The anti-cancer efficacy of radiation therapy is partly attributable to the production of oxyradicals that damage biomolecules. We previously showed that endocrine therapy increases mitochondrial content in ER+ breast cancer cells; we postulated that this may also increase oxidative stress.
Methods: Herein, we tested the efficacy of concurrent endocrine and radiation therapies, including both conventional (CDR) and ultra-high dose rate (UHDR) radiation.
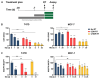
Results: We found that estrogen deprivation and radiation inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, and force cells into an oxidatively stressed state. DNA damage was almost exclusive to cells treated with the combination of endocrine and radiation therapy. Radiation slowed tumor growth in two xenograft models, and combination with estrogen deprivation prolonged the time to regrowth in ZR75-1 tumors.
Conclusions: These findings indicate that simultaneous treatment with endocrine and radiation therapies can be advantageous, warranting further evaluation to identify tumor features predictive of response to individual and combination treatments.
Keywords: antiestrogen; breast cancer; drug-tolerant persisters; endocrine therapy; oxidative stress; radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Darby S., McGale P., Correa C., Taylor C., Arriagada R., Clarke M., Cutter D., Davies C., Ewertz M., Godwin J., et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378:1707–1716. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

