The Telomere Length Signature in Leukemias-From Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Telomere Shortening to Immunotherapeutic Options Against Telomerase
- PMID: 40563586
- PMCID: PMC12190229
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17121936
The Telomere Length Signature in Leukemias-From Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Telomere Shortening to Immunotherapeutic Options Against Telomerase
Abstract
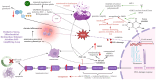
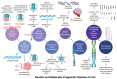
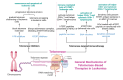
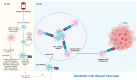
The nucleoprotein structures known as telomeres provide genomic integrity by protecting the ends of chromosomes. Tumorigenesis is associated with alterations in telomere function and stability. This narrative review provides evidence of the potential prognostic value of telomere length and telomerase in leukemias. On the one hand, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction can accelerate telomere shortening, leading to higher susceptibility and the progression of leukemia. On the other hand, cytogenetic alterations (such as gene fusions and chromosomal abnormalities) and genomic complexity can result from checkpoint dysregulation, the induction of the DNA damage response (DDR), and defective repair signaling at telomeres. This review thoroughly outlines the ways by which telomere dysfunction can play a key role in the development and progression of four primary leukemias, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and acute leukemias of myeloid or lymphoid origin, highlighting the potential prognostic value of telomere length in this field. However, telomerase, which is highly active in leukemias, can prevent the rate of telomere attrition. In line with this, leukemia cells can proliferate, suggesting telomerase as a promising therapeutic target in leukemias. For this reason, telomerase-based immunotherapy is analyzed in the fight against leukemias, leveraging the immune system to eliminate leukemia cells with uncontrolled proliferation.
Keywords: genomic instability; immunotherapy in leukemia; leukemia; leukemia prognosis; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress; telomerase inhibitors; telomerase vaccines; telomerase-based therapy; telomere length.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Apetroaei M.-M., Fragkiadaki P., Velescu B.Ș., Baliou S., Renieri E., Dinu-Pirvu C.E., Drăgănescu D., Vlăsceanu A.M., Nedea M.I.I., Udeanu D.I., et al. Pharmacotherapeutic Considerations on Telomere Biology: The Positive Effect of Pharmacologically Active Substances on Telomere Length. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024;25:7694. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

