Comparative Analysis of Microalgae's Physiological Responses to Fibrous and Layered Clay Minerals
- PMID: 40563898
- PMCID: PMC12189120
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14060647
Comparative Analysis of Microalgae's Physiological Responses to Fibrous and Layered Clay Minerals
Abstract
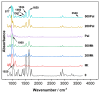
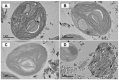
Microalgae interact with mineral particles in an aqueous environment, yet how clay minerals affect physiological processes in algal cells remains unexplored. In this study, we compared the effects of palygorskite (Pal) and montmorillonite (Mt), which respectively represent fibrous and layered clay minerals, on the physiological processes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. It was observed that C. reinhardtii responded differently to the treatments of Pal and Mt. The Pal particles bound tightly to and even inserted themselves into cells, resulting in a significant decrease in cell numbers from 27.35 to 21.02 × 107 mL-1. However, Mt was only loosely attached to the cell surface. The photosynthesis in the algal cells was greatly inhibited by Pal, with the rETRmax significantly reduced from 103.80 to 56.67 μmol electrons m-2s-1 and the downregulation of IF2CP, psbH and OHP1, which are key genes involved in photosynthesis. In addition, Pal reduced the quantities of proteins and polysaccharides in extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) and the P uptake by C. reinhardtii when the P level in the culture was 3.15 mg/L. However, no significant changes were found regarding the above EPS components or the amount of P in algal cells upon the addition of Mt. Together, the impacts of fibrous Pal on C. reinhardtii was more profound than those of layered Mt.
Keywords: 3D-EEM; RNA-Seq; clay minerals; microalgae; physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Griffin J.J., Windom H., Goldberg E.D. The Distribution of Clay Minerals in the World Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1968;15:433–459. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(68)90051-X. - DOI
-
- Li G.L., Zhou C.H., Fiore S., Yu W.H. Interactions between Microorganisms and Clay Minerals: New Insights and Broader Applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019;177:91–113. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.04.025. - DOI
-
- Islam M.R., Singh B., Dijkstra F.A. Stabilisation of Soil Organic Matter: Interactions between Clay and Microbes. Biogeochemistry. 2022;160:145–158. doi: 10.1007/s10533-022-00956-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2022SKL016/State Key Laboratory of Lake Science and Environment
- KYCX21_0570/Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
- 202013YX18/Undergraduate Student Research Training Program in Nanjing Agricultural University
- 202210307114K/Undergraduate Student Research Training Program in Nanjing Agricultural University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

