Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data
- PMID: 40564106
- PMCID: PMC12189552
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13061387
Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data
Abstract
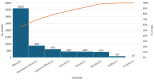
Background/Objectives: During the COVID-19 pandemic, several antivirals were approved or repurposed, but their safety profiles have not been fully compared. Pharmacovigilance data help clarify how these drugs perform in real-world use. Methods: This study performed a comparative pharmacovigilance analysis of eight antivirals used or tested during the COVID-19 pandemic, based on individual case safety reports (ICSRs) retrieved from the EudraVigilance database, reported up to 9 February 2025 and extracted from the official platform on 12 February 2025. Adverse reactions were assessed by system organ class (SOC), demographic patterns, and seriousness, and disproportionality analysis (reporting odds ratio (ROR)) was conducted to identify potential safety signals. Results: A total of 64,776 ICSRs were analyzed. Among approved antivirals, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (NTV/r) accounted for 13.4% (n = 8693) of reports, while remdesivir (RDV) represented 6.3% (n = 4105). Repurposed antivirals such as ribavirin and lopinavir/ritonavir dominated the dataset, together making up over 80% (n = 51,978) of all reports. RDV was associated with a high proportion of serious adverse events (84%, n = 3448), and showed consistent ROR signals in hepatobiliary, renal, cardiac, and general disorders, with values exceeding 2 in several comparisons. NTV/r displayed a milder overall profile, but with positive RORs for psychiatric disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, and product-related issues. The most affected SOCs across all drugs included general disorders (31.6%, n = 20,493), gastrointestinal (19.5%, n = 12,625), nervous system (17.8%, n = 11,511), and investigations (20.4%, n = 13,219). Demographic analysis showed that most events occurred in adults aged 18-64, with RDV more often reported in elderly patients and NTV/r more frequently associated with reports from female patients and non-healthcare reporters. Conclusions: This study highlights distinct pharmacovigilance profiles of COVID-19 antivirals and supports the role of real-world data in guiding safer therapeutic choices.
Keywords: COVID-19; EudraVigilance; antivirals; individual case safety reports; pharmacovigilance; system organ class.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse drug reactions related to methotrexate: a real-world pharmacovigilance study using the FAERS database from 2004 to 2024.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1586361. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1586361. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40534848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cascella M., Rajnik M., Cuomo A., Dulebohn S.C., Di Napoli R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19) [(accessed on 14 April 2025)]; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554776/ - PubMed
-
- COVID-19 Cases, World. World Health Organization COVID-19 Dashboard. [(accessed on 17 April 2025)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c.
-
- Gulick R.M., Pau A.K., Daar E., Evans L., Gandhi R.T., Tebas P., Ridzon R., Masur H., Lane H.C., Adimora A.A., et al. National Institutes of Health COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel: Perspectives and Lessons Learned. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024;177:1547–1557. doi: 10.7326/ANNALS-24-00464. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

