TAAR8 in the Brain: Implications for Dopaminergic Function, Neurogenesis, and Behavior
- PMID: 40564112
- PMCID: PMC12190788
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13061391
TAAR8 in the Brain: Implications for Dopaminergic Function, Neurogenesis, and Behavior
Abstract
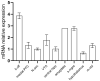
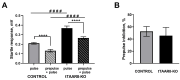
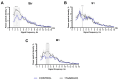
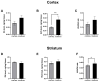
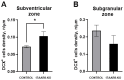
Background/Objectives: G protein-coupled trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs) belong to a family of biogenic amine-sensing receptors. TAAR1 is the best-investigated receptor of this family, and TAAR1 agonists are already being tested in clinical studies for the treatment of schizophrenia, anxiety, and depression. Meanwhile, other TAARs (TAAR2, TAAR5, TAAR6, TAAR8, and TAAR9 in humans) are mostly known for their olfactory function, sensing innate odors. At the same time, there is growing evidence that these receptors may also be involved in brain function. TAAR8 is the least studied TAAR family member, and currently, there is no data on its function in the mammalian central nervous system. Methods: We generated triple knockout (tTAAR8-KO) mice lacking all murine Taar8 isoforms (Taar8a, Taar8b, and Taar8c) using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. In this study, we performed the first phenotyping of tTAAR8-KO mice for behavioral, electrophysiological, and neurochemical characteristics. Results: During the study, we found a number of alterations specific to tTAAR8-KO mice compared to controls. tTAAR8-KO mice demonstrated better short-term memory, more depressive-like behavior, and higher body temperature. Also, we observed changes in the dopaminergic system, brain electrophysiological activity, and adult neurogenic functions in mice lacking Taar8 isoforms. Conclusions: Based on the data obtained, it can be assumed that the physiological TAAR8 role is not limited only to the innate olfactory function, as previously proposed. TAAR8 could be involved in brain function, in particular in dopamine function regulation.
Keywords: TAAR; TAAR8; adult neurogenesis; depression; dopamine; short-term memory; trace amine; triple knockout.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Technological aids for the rehabilitation of memory and executive functioning in children and adolescents with acquired brain injury.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 1;7(7):CD011020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27364851 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4(4):CD009016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27098439 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Borowsky B., Adham N., Jones K.A., Raddatz R., Artymyshyn R., Ogozalek K.L., Durkin M.M., Lakhlani P.P., Bonini J.A., Pathirana S., et al. Trace Amines: Identification of a Family of Mammalian G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2001;98:8966–8971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.151105198. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bunzow J.R., Sonders M.S., Arttamangkul S., Harrison L.M., Zhang G., Quigley D.I., Darland T., Suchland K.L., Pasumamula S., Kennedy J.L., et al. Amphetamine, 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine, Lysergic Acid Diethylamide, and Metabolites of the Catecholamine Neurotransmitters Are Agonists of a Rat Trace Amine Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;60:1181–1188. doi: 10.1124/mol.60.6.1181. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

