Point-of-Care Ultrasound Use in Hemodynamic Assessment
- PMID: 40564145
- PMCID: PMC12189778
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13061426
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Use in Hemodynamic Assessment
Abstract
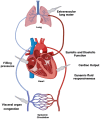
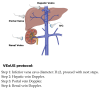
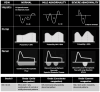
Hemodynamic assessment is critical in emergency and critical care for preventing, diagnosing, and managing shock states that significantly affect patient outcomes. Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) has become an invaluable, non-invasive, real-time, and reproducible tool for bedside decision-making. Advancements such as Doppler imaging, advanced critical care ultrasonography, and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) have expanded its utility, enabling rapid and repeatable evaluations, especially in complex mixed shock presentations. This review explores the role of POCUS in hemodynamic monitoring, emphasizing its ability to assess cardiac output, filling pressures, and vascular congestion, facilitating shock classification and guiding fluid management. We highlight an extensive array of POCUS techniques for evaluating right and left cardiac function and review existing literature on their advantages, limitations, and appropriate clinical applications. Beyond assessing volume status, this review discusses the role of POCUS in predicting fluid responsiveness and supporting more individualized, precise management strategies. Ultimately, while POCUS is a powerful tool for rapid, comprehensive hemodynamic assessment in acute settings, its limitations must be acknowledged and thoughtfully integrated into clinical decision-making.
Keywords: cardiac arrest; critical care; echocardiography; emergency medicine; hemodynamics; point of care; ultrasound; volume assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Experiences of Critical Care Nurses Implementing Point-Of-Care Ultrasound: A Qualitative Study.Nurs Crit Care. 2025 Jul;30(4):e70104. doi: 10.1111/nicc.70104. Nurs Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 40545829
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
The use of Open Dialogue in Trauma Informed Care services for mental health consumers and their family networks: A scoping review.J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024 Aug;31(4):681-698. doi: 10.1111/jpm.13023. Epub 2024 Jan 17. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38230967
-
What is the value of routinely testing full blood count, electrolytes and urea, and pulmonary function tests before elective surgery in patients with no apparent clinical indication and in subgroups of patients with common comorbidities: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effective literature.Health Technol Assess. 2012 Dec;16(50):i-xvi, 1-159. doi: 10.3310/hta16500. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 23302507 Free PMC article.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

