Functional Enrichment Analysis of Rare Mutations in Patients with Brain Arteriovenous Malformations
- PMID: 40564170
- PMCID: PMC12191260
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13061451
Functional Enrichment Analysis of Rare Mutations in Patients with Brain Arteriovenous Malformations
Abstract
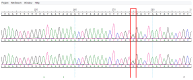
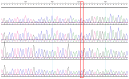
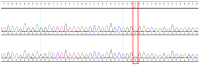
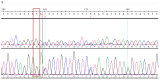
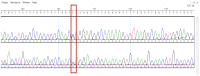
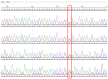
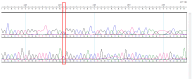
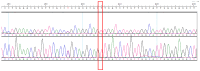
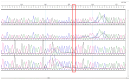
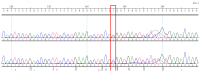
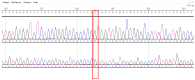
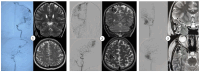
Background/Objectives: Brain arteriovenous malformations (bAVMs) are rare vascular anomalies characterized by direct connections between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary network. This study aimed to identify potential genetic factors contributing to the development of sporadic bAVMs. Methods: Three patients (AVM1-3) from Kazakhstan who underwent microsurgical resection at the National Centre for Neurosurgery (NCN) in Astana, Kazakhstan, were analyzed. Brain AVMs were diagnosed using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Genomic DNA was isolated from whole venous blood samples, and whole-exome sequencing was performed on the NovaSeq 6000 platform (Illumina). Variants were filtered according to standard bioinformatics protocols, and candidate gene prioritization was conducted using the ToppGene tool. Results: In silico analysis further revealed candidate genes likely associated with lesion development, including COL3A1, CTNNB1, LAMA1, NPHP3, SLIT2, SLIT3, SMO, MAPK3, LRRK2, TTN, ERBB2, PARD3, and OBSL1. It is essential to focus on the genetic variants affecting the following prioritized genes: ERBB2, SLIT3, SMO, MAPK3, and TTN. Mutations in these genes were predicted to be "damaging". Most of these genes are involved in signaling pathways that control vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Conclusions: Defects in genes associated with ciliary structure and function may be critical to the pathogenesis of brain AVMs. These findings provide valuable insights into the molecular underpinnings of bAVM development, emphasizing key biological pathways and potential candidate genes. Further research is needed to establish robust correlations between specific genetic mutations and clinical phenotypes, which could ultimately inform the development of improved diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic approaches.
Keywords: brain arteriovenous malformation; candidate genes; enrichment analysis; exome sequencing; mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD000213. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000213. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 07;(4):CD000213. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000213.pub2. PMID: 12917889 Updated.
References
-
- Pinheiro L.C.P., Wolak Junior M., Ferreira M.Y., Magalhaes R.B., Fernandes A.Y., Paiva W.S., Zanini M.A., Marchesan Rodrigues M.A. Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mortality and Morbidity in Aruba-Eligible Studies. World Neurosurg. 2024;185:381–392.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.02.109. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bokhari M.R., Bokhari S.R.A. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; St. Petersburg, FL, USA: 2025. Arteriovenous Malformation of the Brain. - PubMed
-
- Bharatha A., Faughnan M.E., Kim H., Pourmohamad T., Krings T., Bayrak-Toydemir P., Pawlikowska L., McCulloch C.E., Lawton M.T., Dowd C.F., et al. Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Multiplicity Predicts the Diagnosis of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Quantitative Assessment. Stroke. 2012;43:72–78. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.629865. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

