Ketone Body Induction: Insights into Metabolic Disease Management
- PMID: 40564203
- PMCID: PMC12191297
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13061484
Ketone Body Induction: Insights into Metabolic Disease Management
Abstract
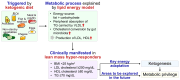
Ketone bodies (KBs), particularly β-hydroxybutyrate, are crucial metabolites that provide clean and efficient energy, especially during periods of low glucose availability. Ketogenesis is a promising therapeutic avenue for conditions such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes. This review aims to summarize the current evidence on ketogenesis across different health conditions and therapeutic modalities, highlighting the potential to mitigate metabolic disorders and diabetes-related complications. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, increased KB production provides cardiovascular and neuroprotective benefits. Ketogenesis is enhanced under physiological conditions like pregnancy and fasting, as well as in pathophysiological states such as diabetes and heart failure. Various interventions, including the promotion of endogenous ketogenesis through diet and exercise, drug-induced ketogenesis via sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and exogenous ketone supplementation, have demonstrated favorable effects on metabolic health. However, challenges remain, including risks such as pathological ketoacidosis and dyslipidemia. In specific populations, such as lean mass hyper-responders, laboratory lipid profiles might reflect the metabolic privilege. This review will assist in the future clarification of individual differences and optimized therapeutic approaches leveraging ketogenesis for the personalized management of metabolic disorders.
Keywords: diabetes; ketogenesis; ketone bodies; metabolic diseases; β-hydroxybutyrate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effects of ketone bodies and ketogenesis on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway: A systematic review.Nutr Res. 2025 Jul;139:16-49. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2025.04.010. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Nutr Res. 2025. PMID: 40381609
-
Global consensus on optimal exercise recommendations for enhancing healthy longevity in older adults (ICFSR).J Nutr Health Aging. 2025 Jan;29(1):100401. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2024.100401. Epub 2025 Jan 1. J Nutr Health Aging. 2025. PMID: 39743381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health promotion lifestyle interventions for weight management in psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BMC Psychiatry. 2012 Jul 12;12:78. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-78. BMC Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22789023 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
AGA Clinical Practice Update on GI Manifestations and Autonomic or Immune Dysfunction in Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: Expert Review.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jul;23(8):1291-1302. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.02.015. Epub 2025 May 19. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40387691 Review.
Cited by
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors: From Structure-Effect Relationship to Pharmacological Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 19;26(14):6937. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146937. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

