Prescribing Antidiabetic Medications Among GPs in Croatia-A Real-Life Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 40564210
- PMCID: PMC12190737
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13061491
Prescribing Antidiabetic Medications Among GPs in Croatia-A Real-Life Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
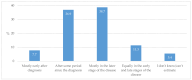
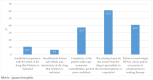
Background: Advances in the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in recent decades have been primarily focused on its broader understanding in the context of the possibility of preventing the development and progression of the disease and of cardiovascular (CV) complications. Nevertheless, worldwide research indicates that individuals with T2D are still under-regulated, both in terms of glycemic control and in preventing CV complications. The aim of this study was to examine Croatian general practitioners (GPs)' practice and patterns in prescribing antidiabetic medications and their understanding of guidelines. Methods: Research was conducted using a self-designed anonymous survey, which was delivered to the e-mail addresses of GPs throughout Croatia in digital format. Respondents were solely GPs, without any restrictions with regard to their characteristics. Data on the number of individuals diagnosed with T2D and prescribed a specific medication were based on declarations by respondents from their e-health records. Results: Approximately 59% of individuals with T2D are cared for solely by GPs. In terms of achieving targeted values of HbA1c, 47% of individuals with T2D are well regulated. Almost all the respondents claim that they review prescribed T2D therapy at least once a year. A total of 47.6% of respondents have read and entirely understood the EASD/ADA guidelines, but 58.3% apply the dual principles of controlling HbA1c levels and CV risk in the treatment of T2D. In individuals with associated CV comorbidity, SGLT2ins were the most frequently prescribed. Conclusions: The results indicate that Croatian GPs are still inclined to apply outdated paradigms of T2D treatment but that they are gradually accepting new regimens of care and recommendations for prescribing novel, more effective medications.
Keywords: GLP-1 RAs; SGLT2ins; cardiovascular risk; family medicine; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures











Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

