Antimicrobial Resistance in European Companion Animals Practice: A One Health Approach
- PMID: 40564260
- PMCID: PMC12189186
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15121708
Antimicrobial Resistance in European Companion Animals Practice: A One Health Approach
Abstract
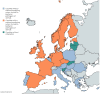
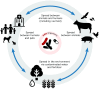
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global health emergency. The growing levels of multidrug-resistant bacteria in companion animals represent a critical but under-recognized threat, as pets can act as reservoirs and vectors of resistant pathogens, and bacteria can spread between species. Despite living in close proximity to humans and sharing many of the same antibiotic classes, companion animals remain largely overlooked in the AMR control strategies. A major obstacle to combating AMR in Europe is the absence of a mandatory and uniform surveillance system. Without a standardized approach, data collection remains inconsistent, leading to knowledge gaps and hindering effective investigation and policymaking. Surveillance failures prevent a comprehensive understanding of resistance patterns, making it difficult to implement timely and evidence-based measures. Existing laws and regulations are insufficient to contain the growing threat of AMR. Current policies fail to enforce strict antimicrobial stewardship across all European countries and lack the necessary scope to address resistance effectively. Urgent action is required-Europe must implement stronger, harmonized surveillance systems, enforce stricter veterinary antimicrobial regulations, and develop more active and binding programs to curb resistance before it reaches an uncontrollable level. A One Health approach, recognizing the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, is essential.
Keywords: One Health; antibiotic resistance; antibiotics; companion animals; humans; veterinary medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Joosten P., Ceccarelli D., Odent E., Sarrazin S., Graveland H., Van Gompel L., Battisti A., Caprioli A., Franco A., Wagenaar J.A., et al. Antimicrobial Usage and Resistance in Companion Animals: A Cross-Sectional Study in Three European Countries. Antibiotics. 2020;9:87. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9020087. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cassini A., Högberg L.D., Plachouras D., Quattrocchi A., Hoxha A., Simonsen G.S., Colomb-Cotinat M., Kretzschmar M.E., Devleesschauwer B., Cecchini M., et al. Attributable Deaths and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years Caused by Infections with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A Population-Level Modelling Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019;19:56–66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fariñas-Guerrero F., Villatoro A.J., Martinez-Manzanares E., López-Gigosos R. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Colonization among Veterinarians in the Province of Malaga, Spain. Vet. World. 2024;17:2719–2724. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.2719-2724. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

