e-Health Strategy for Surgical Prioritization: A Methodology Based on Digital Twins and Reinforcement Learning
- PMID: 40564421
- PMCID: PMC12189496
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12060605
e-Health Strategy for Surgical Prioritization: A Methodology Based on Digital Twins and Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
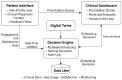
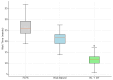
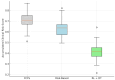
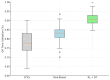
This article presents a methodological framework for elective surgery scheduling based on the integration of patient-specific Digital Twins (DTs) and reinforcement learning (RL). The proposed approach aims to support the future development of an intelligent e-health platform for dynamic, data-driven prioritization of surgical patients. We generate prioritization scores by modeling clinical, economic, behavioral, and social variables in real time and optimize access through a reinforcement learning engine designed to maximize long-term system performance. The methodology is designed as a modular, transparent, and interoperable digital decision-support architecture aligned with the goals of organizational transformation and equitable healthcare delivery. To validate its potential, we simulate realistic surgical scheduling scenarios using synthetic patient data. Results demonstrate substantial improvements compared withto traditional strategies, including a 55.1% reduction in average wait time, a 41.9% decrease in clinical risk at surgery, a 16.1% increase in OR utilization, and a significant increase in the prioritization of socially vulnerable patients. These findings highlight the value of the proposed framework as a foundation for future smart healthcare platforms that support transparent, adaptive, and ethically aligned decision-making in surgical scheduling.
Keywords: Digital Twin; digital decision support; e-Health platform; equitable access; intelligent scheduling; reinforcement learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aitken S.J., James S., Lawrence A., Glover A., Pleass H., Thillianadesan J., Monaro S., Hitos K., Naganathan V. Codesign of health technology interventions to support best-practice perioperative care and surgical waitlist management. BMJ Health Care Inform. 2024;31:e100928. doi: 10.1136/bmjhci-2023-100928. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koushan M. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Otago; Dunedin, New Zealand: 2022. Improving Surgical Service Delivery: Managing Surgery Cancellations with Comprehensive Scheduling and Simulation of Operating Room Capacity Management Policies.
-
- Sigurpálsson Á.Ö. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Iceland; Reykjavik, Iceland: 2025. Pattern Scheduling: A Practical Approach to Preventing Surgery Cancellations Due to Uncertainty in Surgery Times, Bed Availability, and Arrivals of Semi-Acute Elective Patients.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

