MRI-Based Machine Learning and Radiomics Methods for Assessing Spinal Cord Function in Patients with Mild Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
- PMID: 40564482
- PMCID: PMC12189521
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12060666
MRI-Based Machine Learning and Radiomics Methods for Assessing Spinal Cord Function in Patients with Mild Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
Abstract
(1) Background: Patients with mild cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) who delay surgery risk progression. While PET evaluates spinal cord function, its cost and radiation limit its use. (2) Methods: In this prospective study, patients with mild cervical spondylosis underwent preoperative 18F-FDG PET-MRI. Narrowed spinal levels were classified based on whether SUVmax was decreased. Follow-up assessments were conducted. Two machine learning models using MRI T2-based radiomics were developed to identify stenotic levels and decreased SUVmax. (3) Results: Patients with normal SUVmax showed greater symptom improvement. The radiomics models performed well, with AUCs of 0.981/0.962 (training/testing) for stenosis detection and 0.830/0.812 for predicting SUVmax decline. The model outperformed clinicians in predicting SUVmax decline, improving the AUC by 10%. (4) Conclusion: Patients with preserved SUVmax have better outcomes. MRI-based radiomics shows potential for identifying stenosis and predicting spinal cord function changes for preoperative assessment, though larger studies are needed to validate its clinical utility.
Keywords: PET-MRI; cervical spondylotic myelopathy; machine learning; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
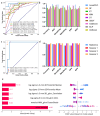
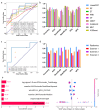
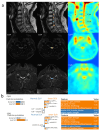
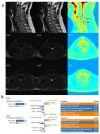
References
-
- Rhee J., Tetreault L.A., Chapman J.R., Wilson J.R., Smith J.S., Martin A.R., Dettori J.R., Fehlings M.G. Nonoperative versus operative management for the treatment degenerative cervical myelopathy: An updated systematic review. Glob. Spine J. 2017;7((Suppl. 3)):35S–41S. doi: 10.1177/2192568217703083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aiello M., Alfano V., Salvatore E., Cavaliere C., Picardi M., Della Pepa R., Nicolai E., Soricelli A., Vella A., Salvatore M., et al. [18F] FDG uptake of the normal spinal cord in PET/MR imaging: Comparison with PET/CT imaging. EJNMMI Res. 2020;10:91. doi: 10.1186/s13550-020-00680-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

