Unveiling the Power of Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Game-Changer in Late-Onset Neonatal Sepsis Diagnosis
- PMID: 40564645
- PMCID: PMC12191239
- DOI: 10.3390/children12060687
Unveiling the Power of Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Game-Changer in Late-Onset Neonatal Sepsis Diagnosis
Abstract
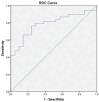
Background/Objectives: The present study evaluated the diagnostic utility of underutilized parameters derived from complete blood count (CBC) analysis in identifying late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS). The parameters evaluated included the nucleated red blood cell count (NRBC), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), red cell distribution width (RDW), plateletcrit (PCT), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR). Methods: This was a retrospective, single-center, case-control study in a tertiary neonatal intensive care unit. The study included 38 neonates diagnosed with LOS, and 22 healthy control subjects. The data collected encompassed demographic characteristics, clinical findings, and laboratory values, including complete blood count (CBC)-derived parameters, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and blood cultures. Statistical analyses were performed to assess differences between groups and the diagnostic performance of key parameters via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Results: The results of the study are as follows: A set of notable discrepancies were identified in a number of parameters when comparing the LOS and control groups. Elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), platelet count, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), lymphocyte percentage, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were found to be associated with LOS. Concurrently, decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, neutrophil percentage, NRBC percentage, and NLR were also associated with LOS. PLR exhibited the most robust diagnostic efficacy, with a cutoff value of 45.24 attaining 81.6% sensitivity, 61.9% specificity, and an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.787 (95% CI: 0.671-0.903). The application of a logistic regression analysis indicated that the PLR emerged as the most salient independent predictor of LOS (odds ratio [OR]: 1.071; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.009-1.135; p = 0.023). Conclusions: CBC-derived parameters, particularly the PLR, have been shown to offer promising diagnostic value for LOS. These findings support the incorporation of these accessible and cost-effective biomarkers into clinical practice for the early diagnosis and management of LOS, warranting further validation in larger, multicenter studies.
Keywords: NLR; PLR; late-onset neonatal sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tunç T., Polat A., Özdemir R., Kiliçaslan B., Can E., Çelik H.T., Arsan S., Kader Ş., Erol S., Uslu S. Assessment of novel biomarkers: sTREM-1, pentraxin-3 and pro-adrenomedullin in the early diagnosis of neonatal early onset sepsis. J. Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2020;13:47–54. doi: 10.3233/NPM-180131. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous