The Impact of Early Cranial Doppler Ultrasonography on Prognosis in Neonates with Perinatal Asphyxia
- PMID: 40564703
- PMCID: PMC12191212
- DOI: 10.3390/children12060745
The Impact of Early Cranial Doppler Ultrasonography on Prognosis in Neonates with Perinatal Asphyxia
Abstract
Background: Cranial Doppler ultrasonography (DS) is a non-invasive method for evaluating cerebral hemodynamics in neonates with perinatal asphyxia (PA). This study aimed to assess whether cerebral vascular resistance indices (RIs) measured within the first 24 h of life can predict the severity of brain injury.
Methods: DS was performed on the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA) between 6 and 24 h after birth in newborns diagnosed with PA. Prognostic value was evaluated by comparing RI values with cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results.
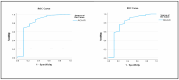
Results: Of the 107 infants included in the study, 11 (10.3%) had severe brain damage, 27 (25.2%) had mild and 20 (18.7%) had moderate changes. The mean ACA RI was 0.61 ± 0.15 in the severe group and 0.70 ± 0.12 in the mild-moderate group (p = 0.023). MCA RI was 0.63 ± 0.20 and 0.71 ± 0.13, respectively. ROC analysis showed an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.901 for ACA RI with a cut-off of 0.58 (84% sensitivity and 84% specificity), and 0.874 for MCA RI with a cut-off of 0.59 (83% sensitivity and 84% specificity).
Conclusions: Early ACA and MCA RI measurements via Doppler ultrasonography may serve as valuable predictors of brain injury severity in neonates with PA and should be considered alongside other clinical and imaging findings.
Keywords: Doppler USG; neonatal; perinatal asphyxia; resistive index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Cerebral Saturation and Fractional Tissue Oxygen Extraction Are Associated with Anterior Cerebral Artery Doppler Parameters in Neonates with Congenital Heart Defects.Neonatology. 2025 May 30:1-9. doi: 10.1159/000546675. Online ahead of print. Neonatology. 2025. PMID: 40451174 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent auscultation (IA) of fetal heart rate in labour for fetal well-being.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 13;2(2):CD008680. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008680.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28191626 Free PMC article.
-
Planned early birth versus expectant management (waiting) for prelabour rupture of membranes at term (37 weeks or more).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 4;1(1):CD005302. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005302.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28050900 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic accuracy of cerebroplacental ratio and middle cerebral artery Doppler for adverse perinatal outcome: systematic review and meta-analysis.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Mar;51(3):313-322. doi: 10.1002/uog.18809. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 28708272 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet count, spleen length, and platelet count-to-spleen length ratio for the diagnosis of oesophageal varices in people with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 26;4(4):CD008759. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008759.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28444987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee A.C., Kozuki N., Blencowe H., Vos T., Bahalim A., Darmstadt G.L., Niermeyer S., Ellis M., Robertson N.J., Cousens S., et al. Intrapartum-related neonatal encephalopathy incidence and impairment at regional and global levels for 2010 with trends from 1990. Pediatr. Res. 2013;74((Suppl. S1)):50–72. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources